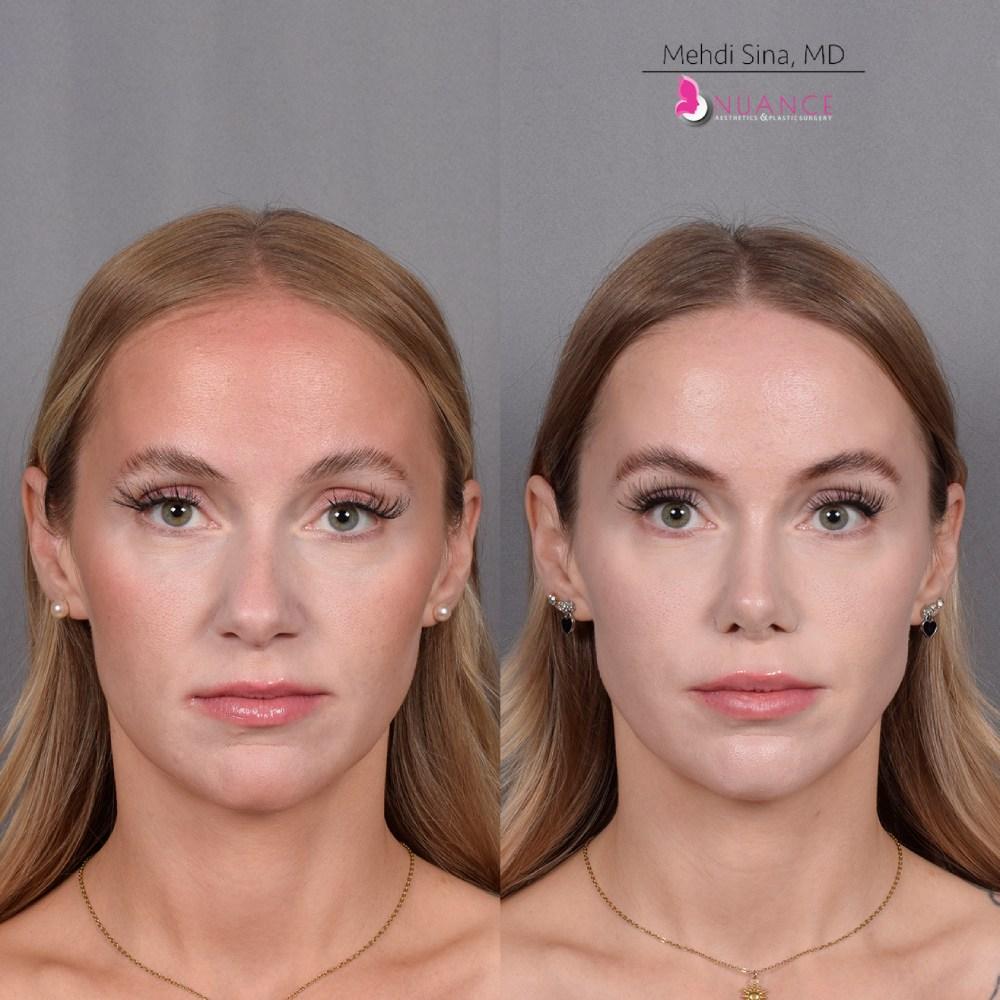
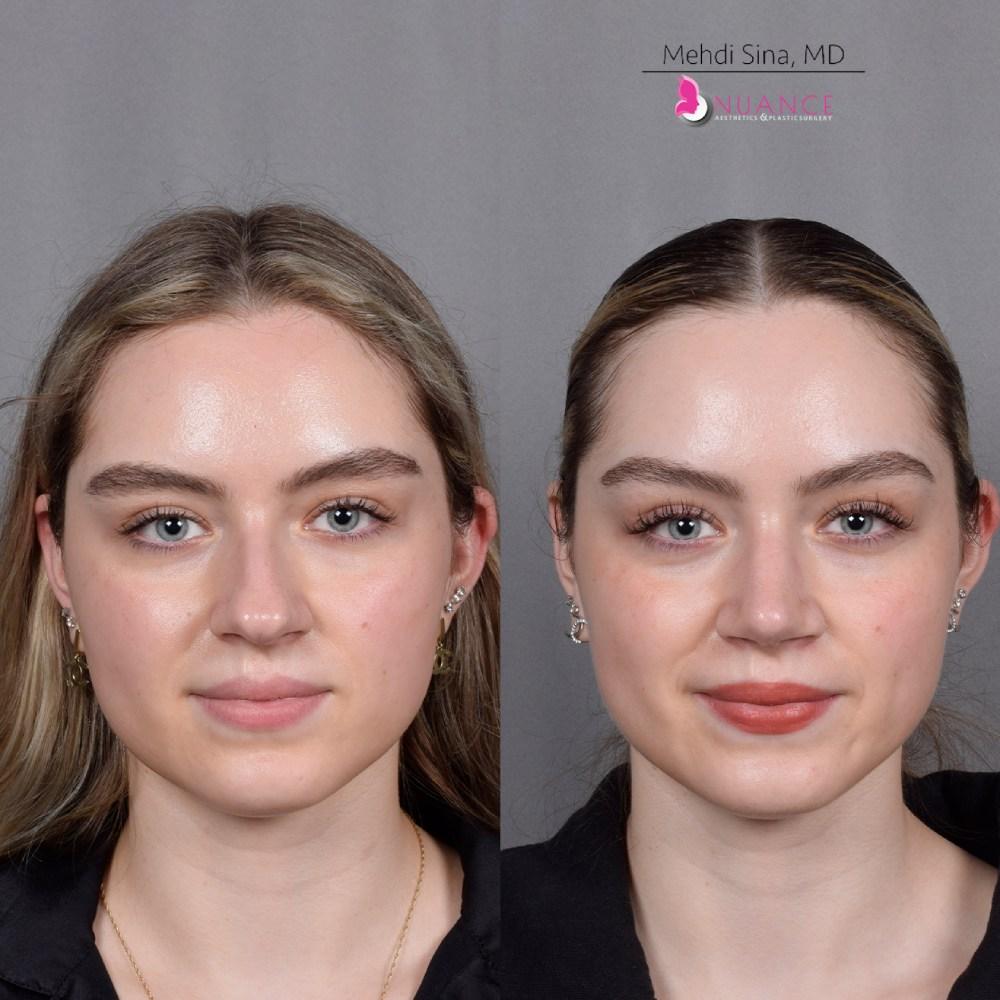
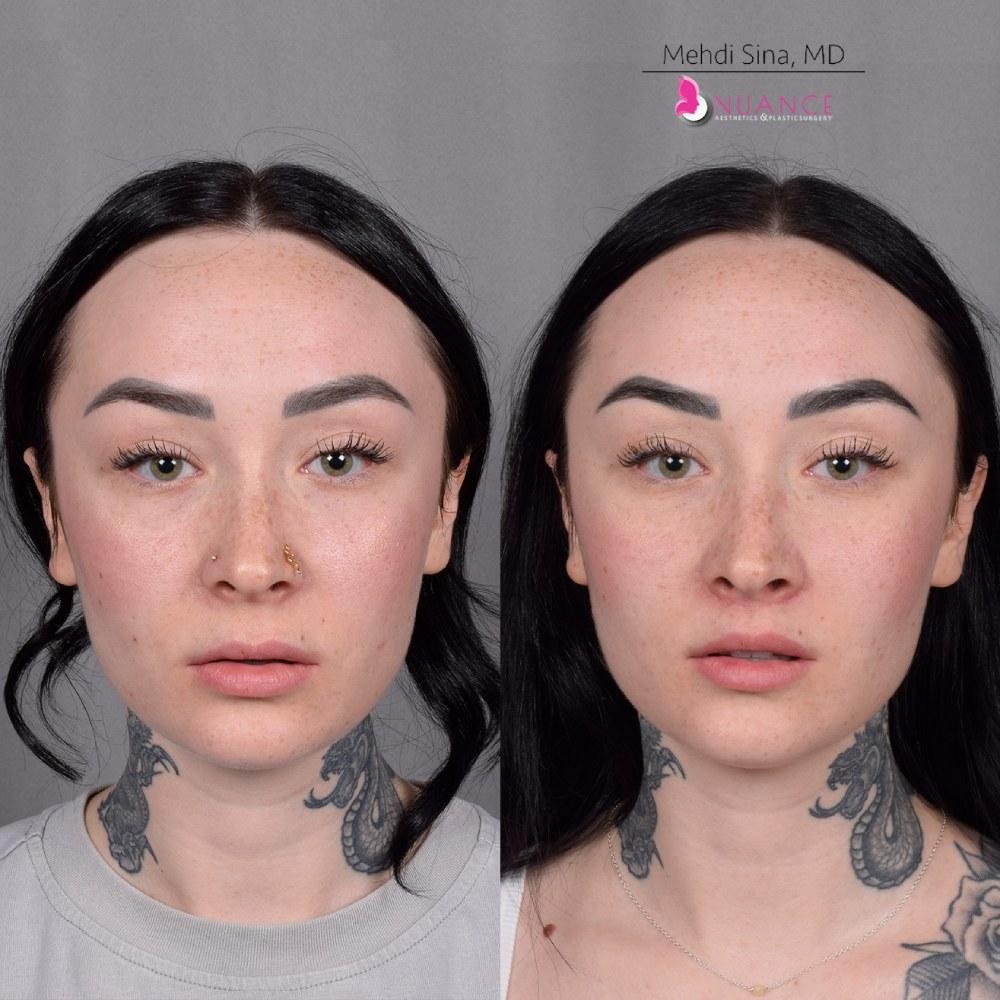
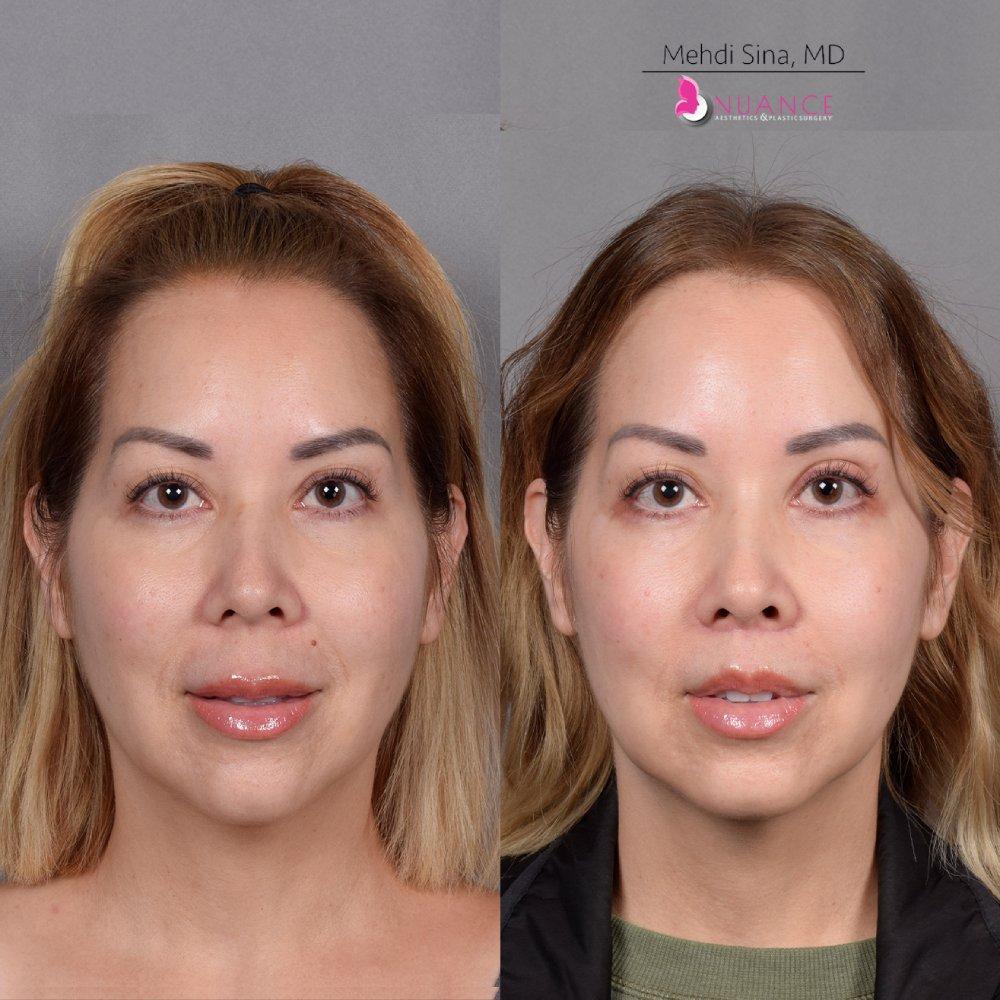
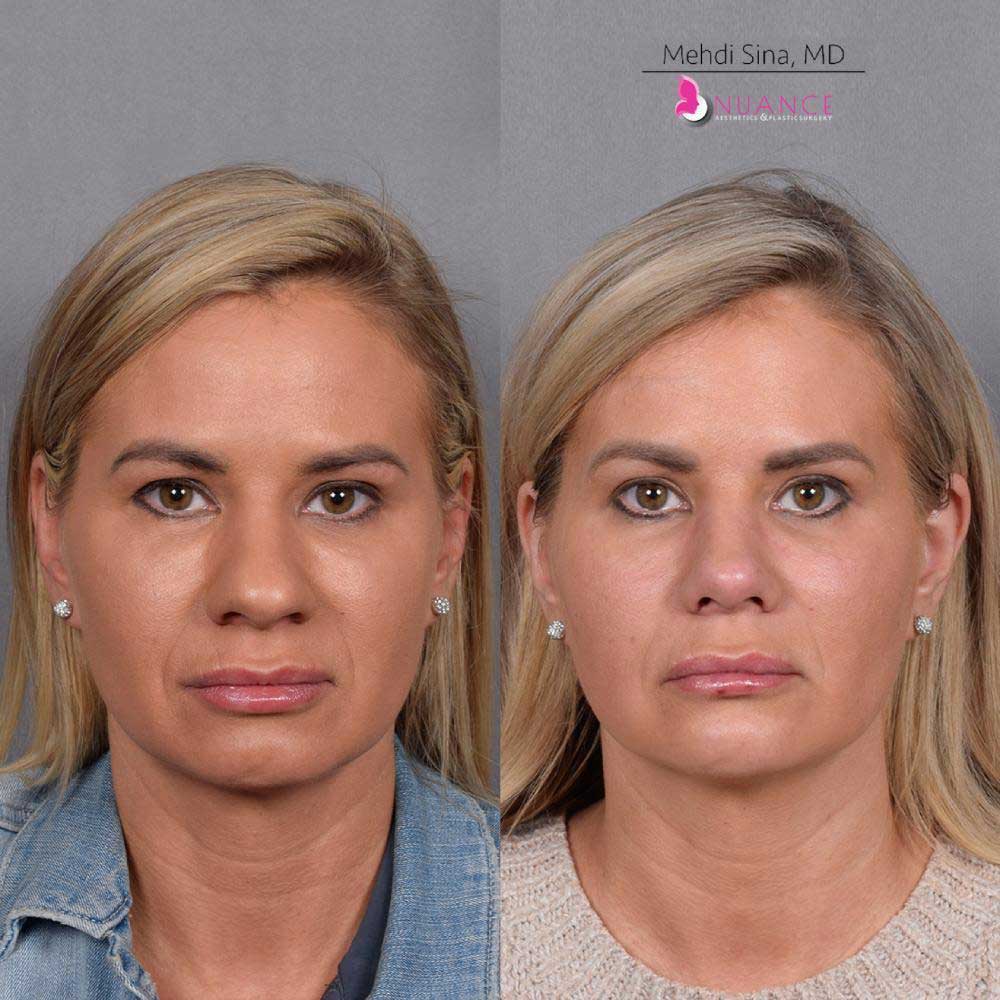
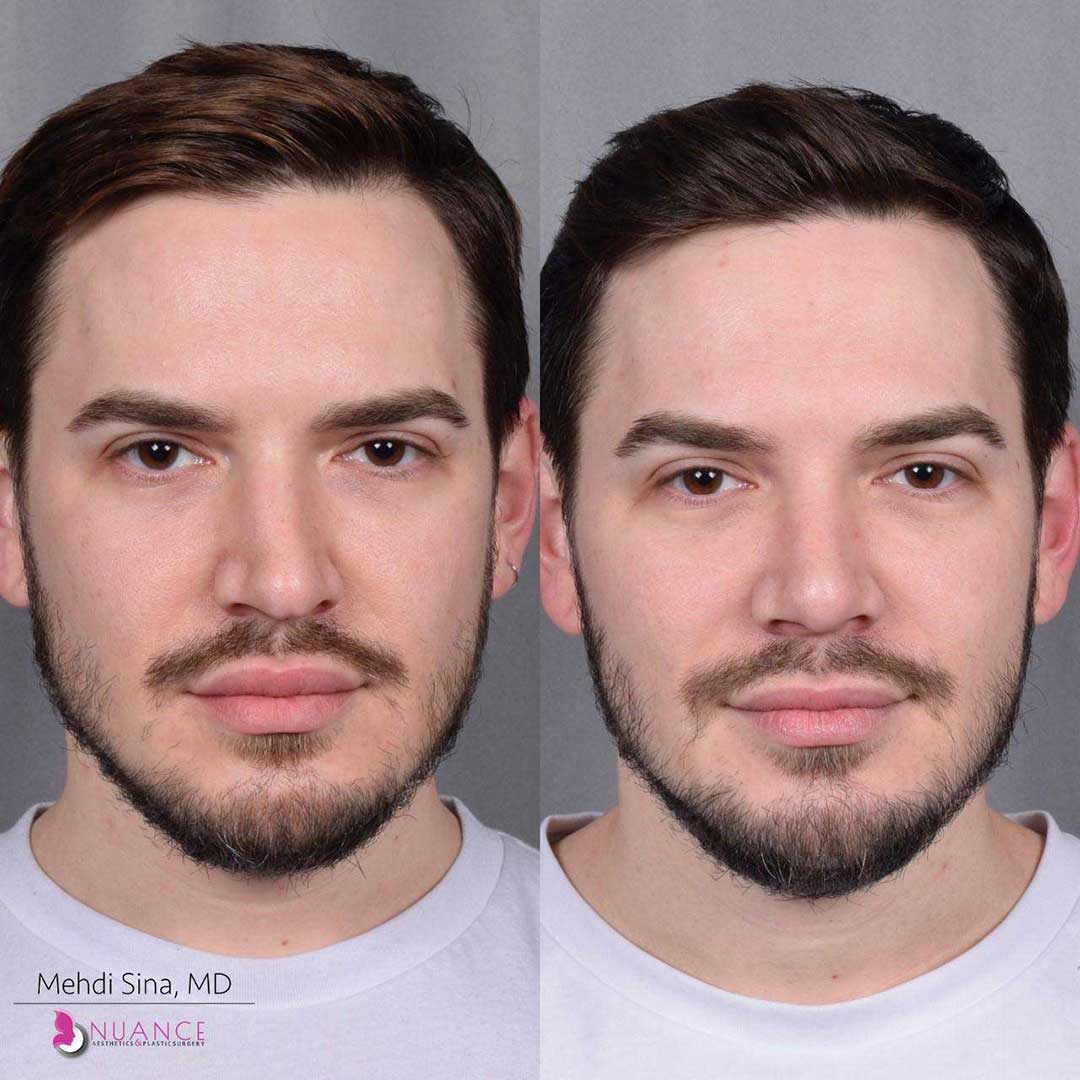
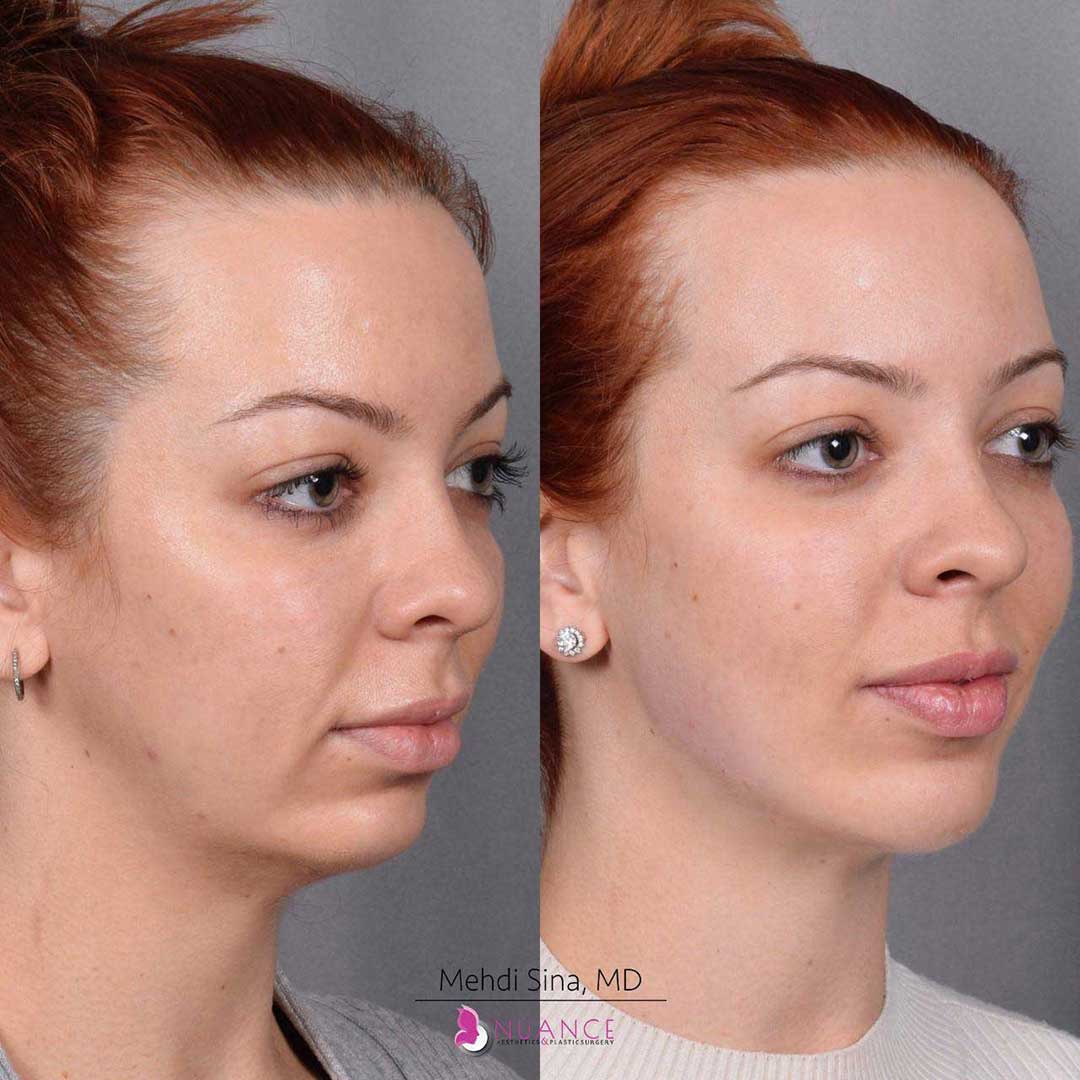
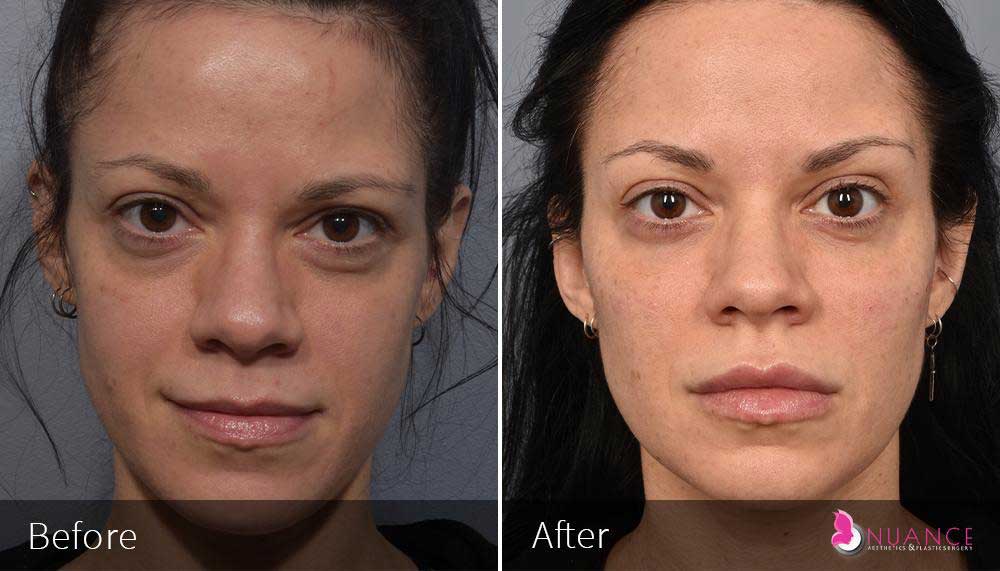
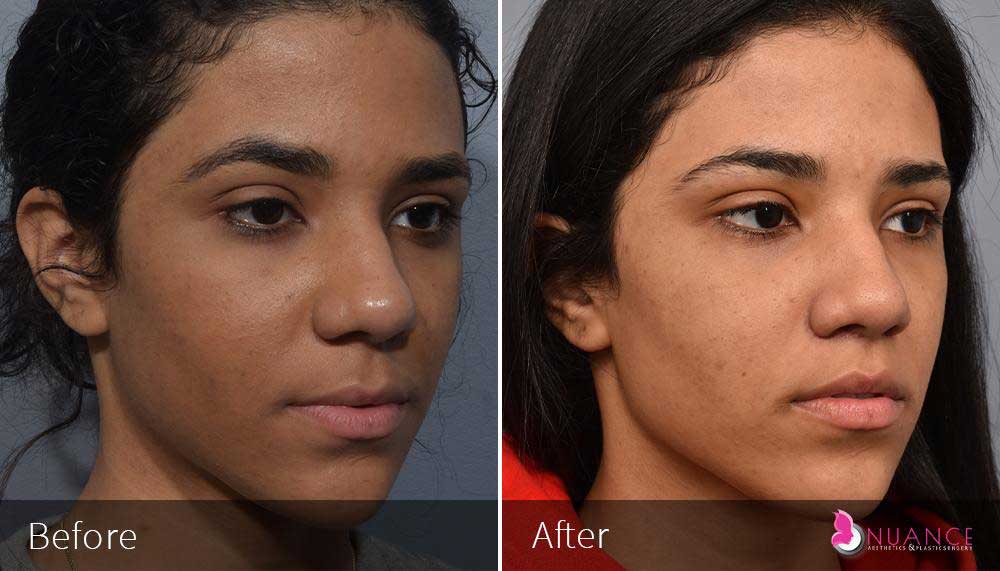
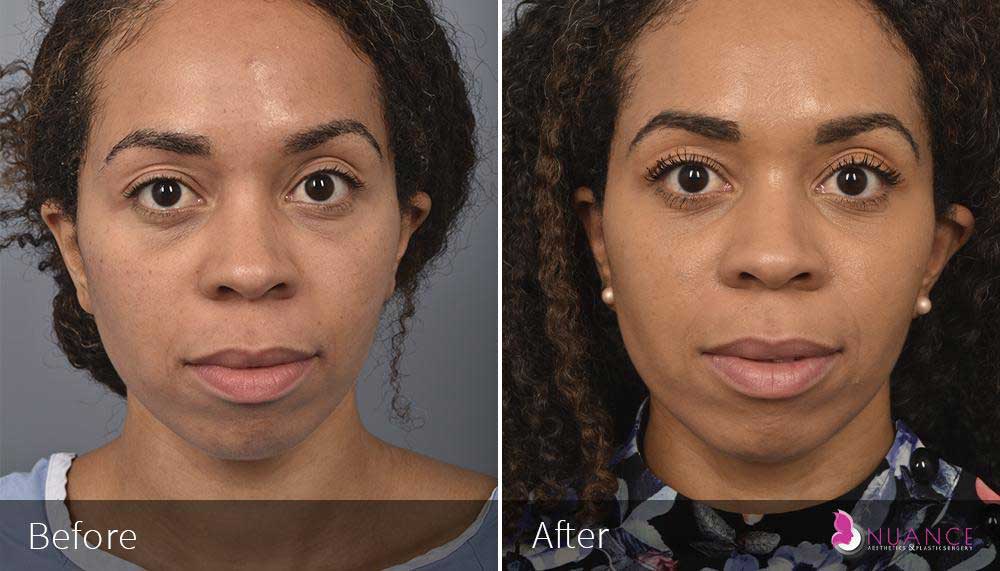
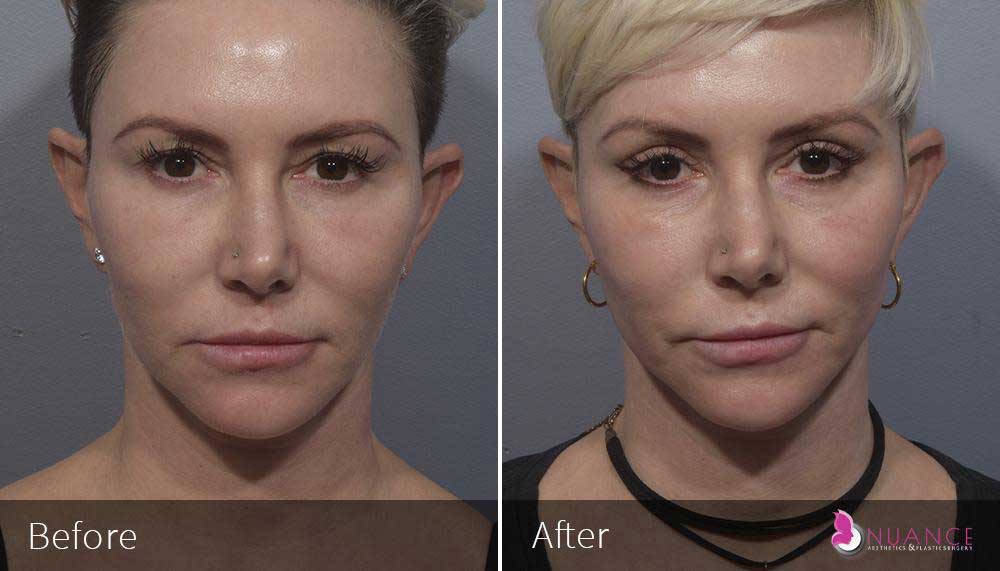
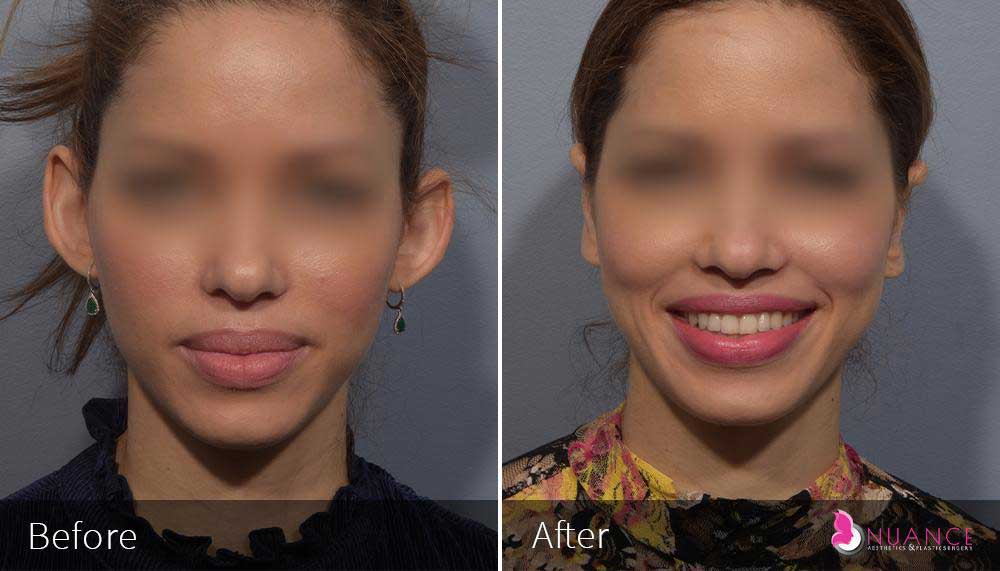
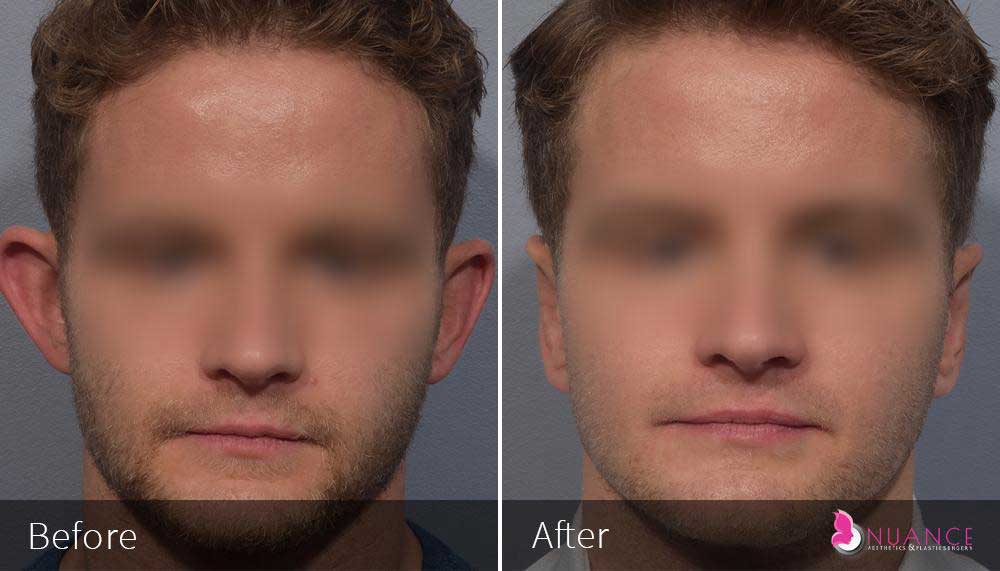
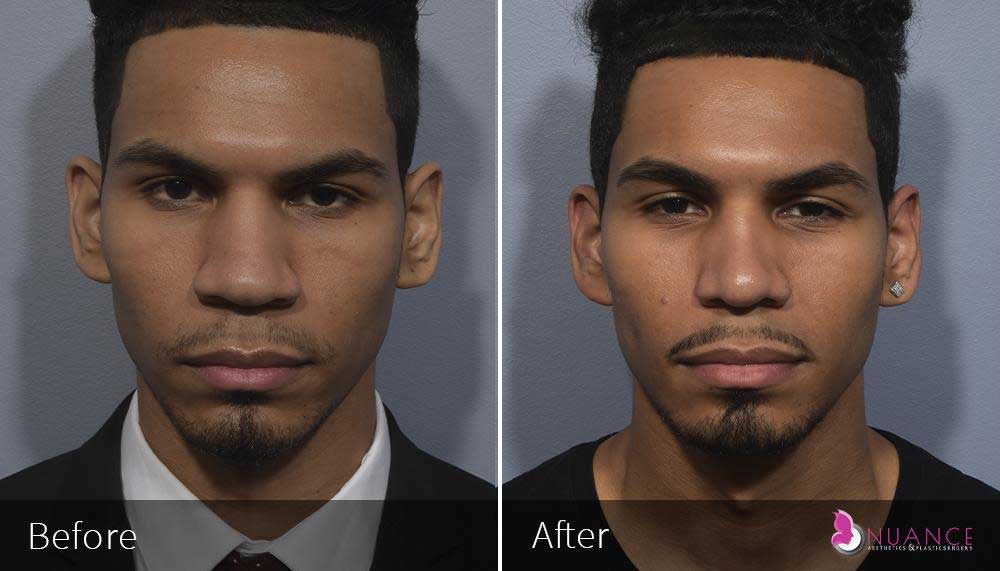
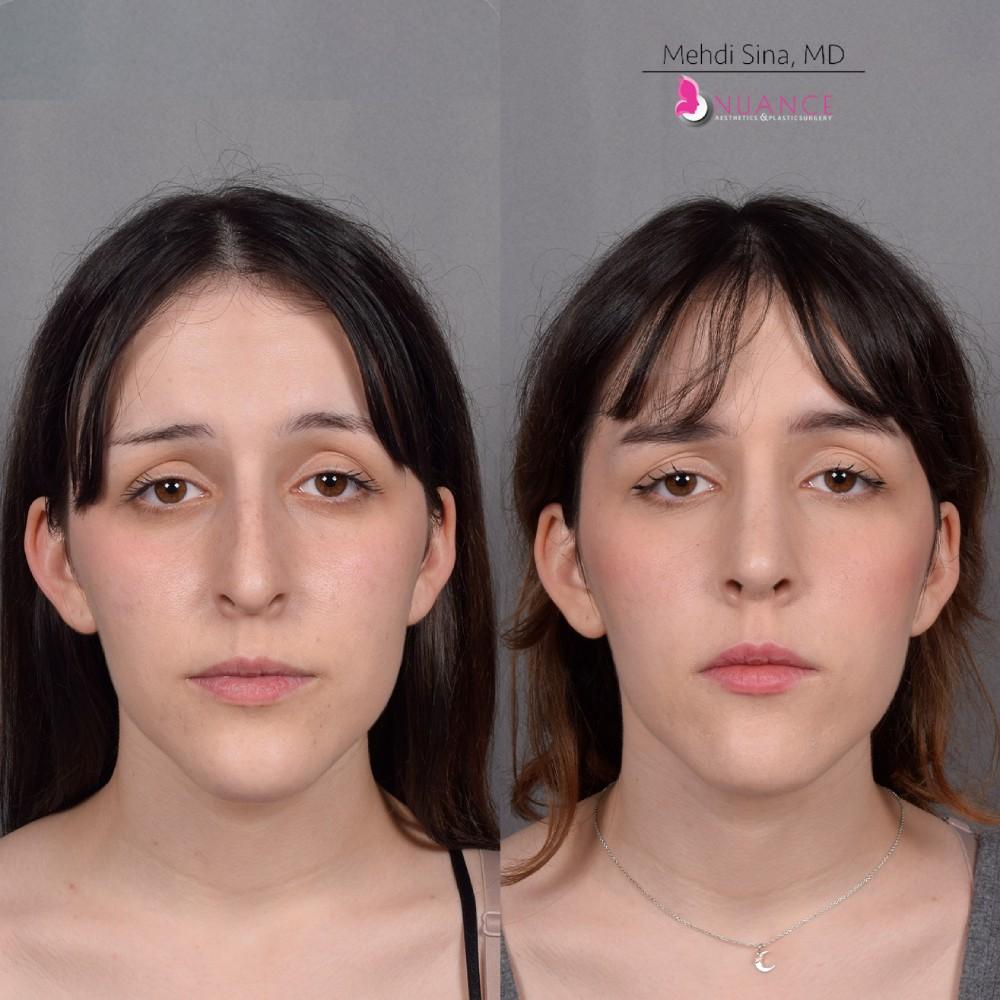
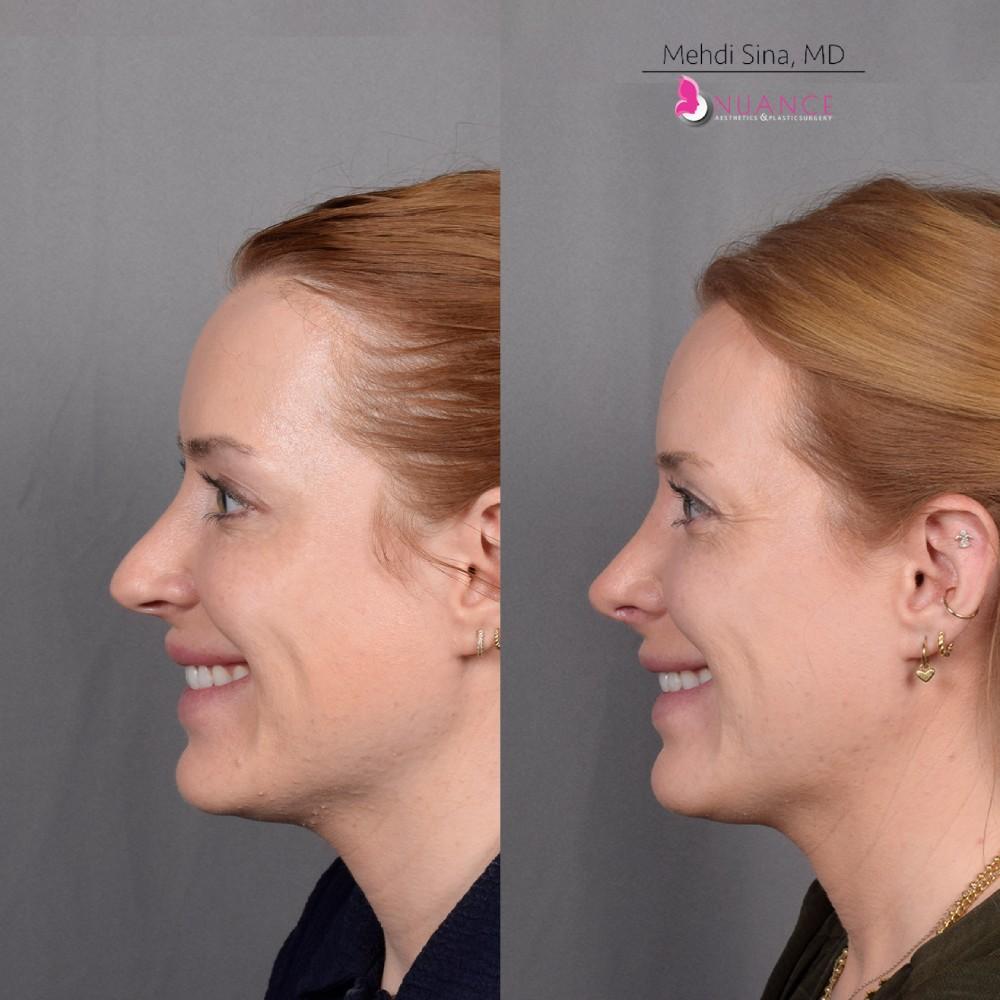
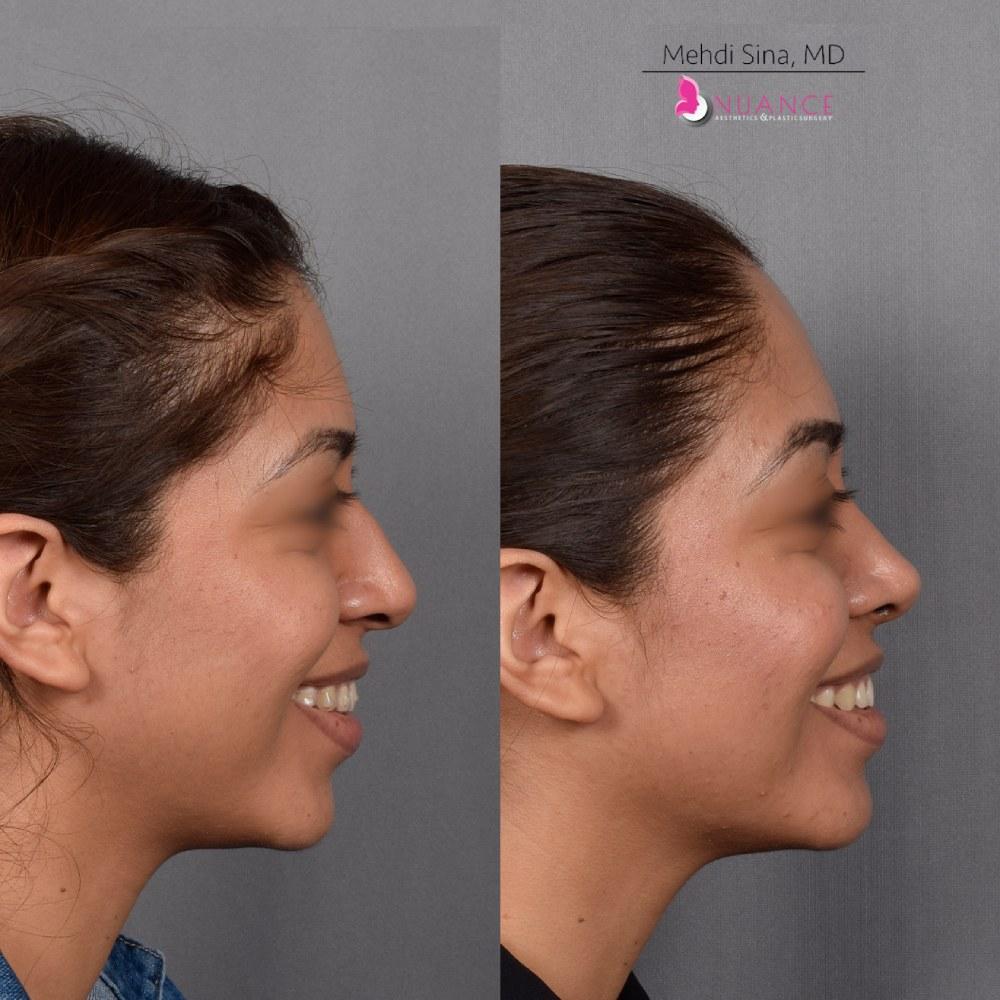
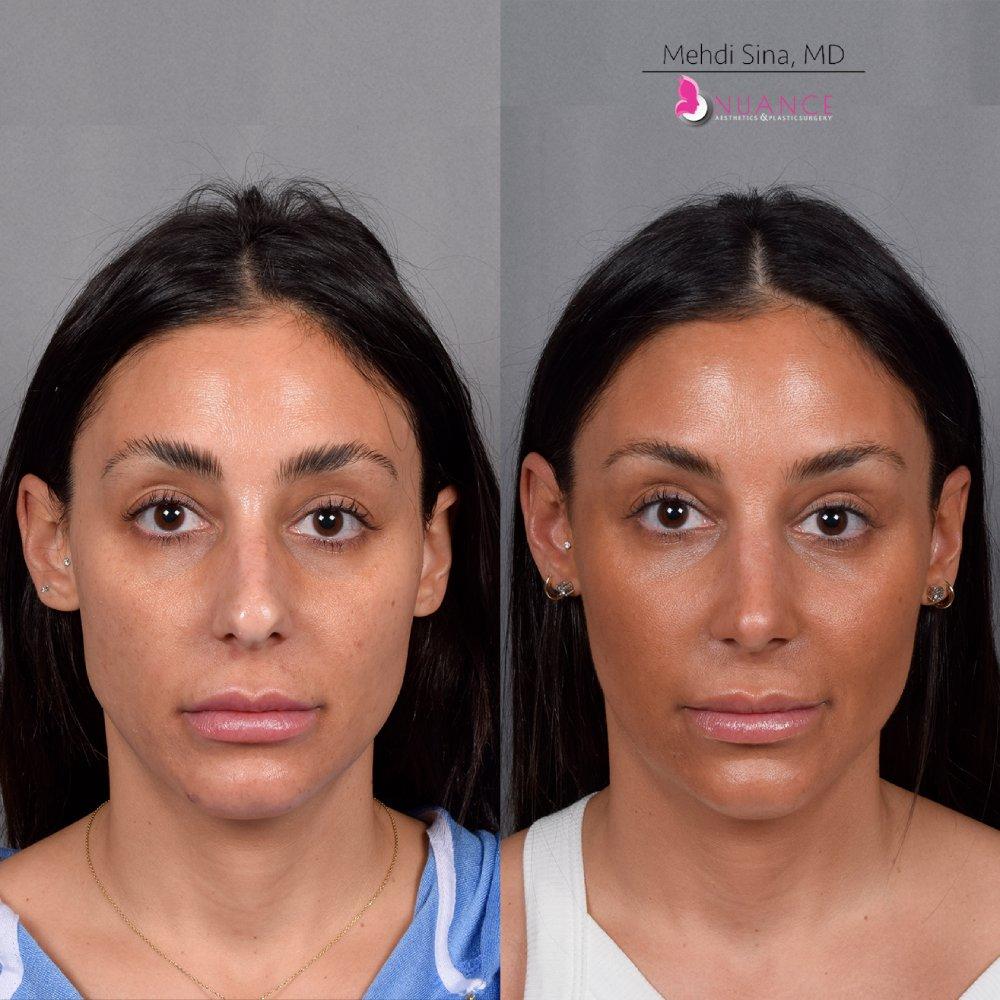
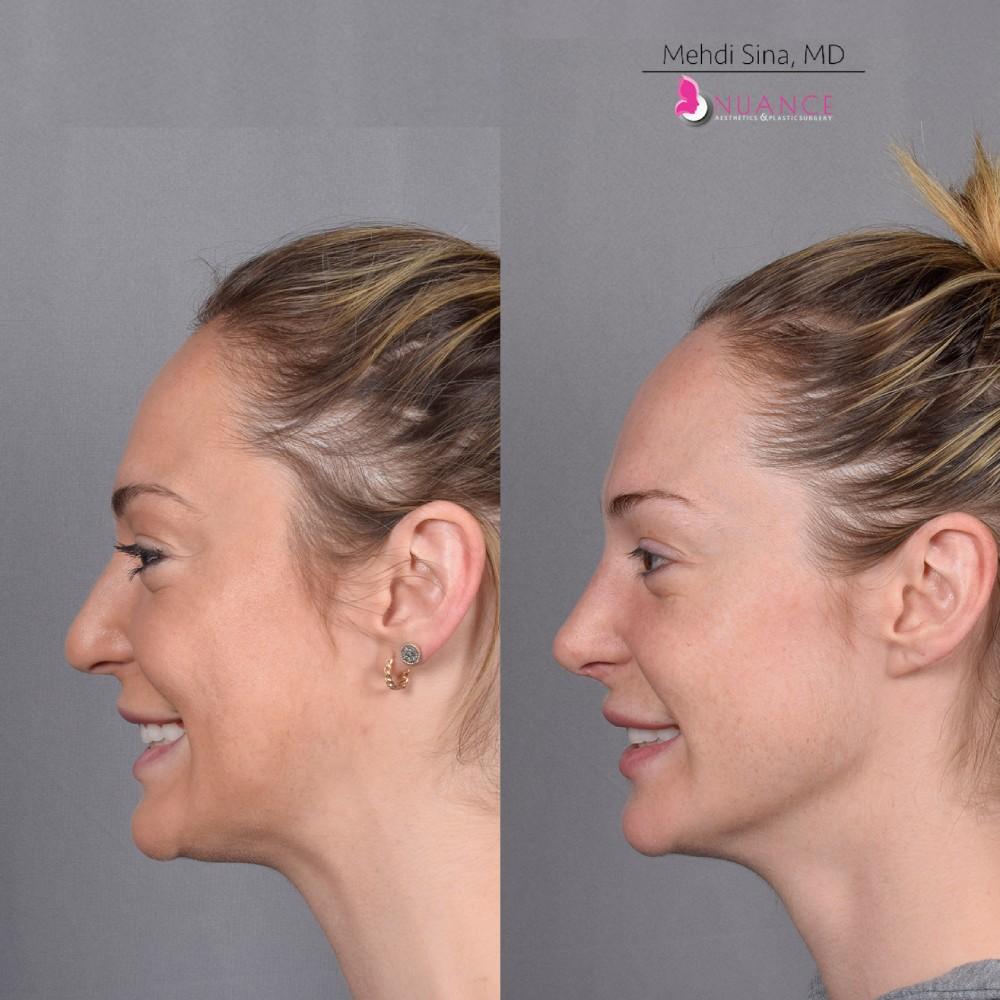
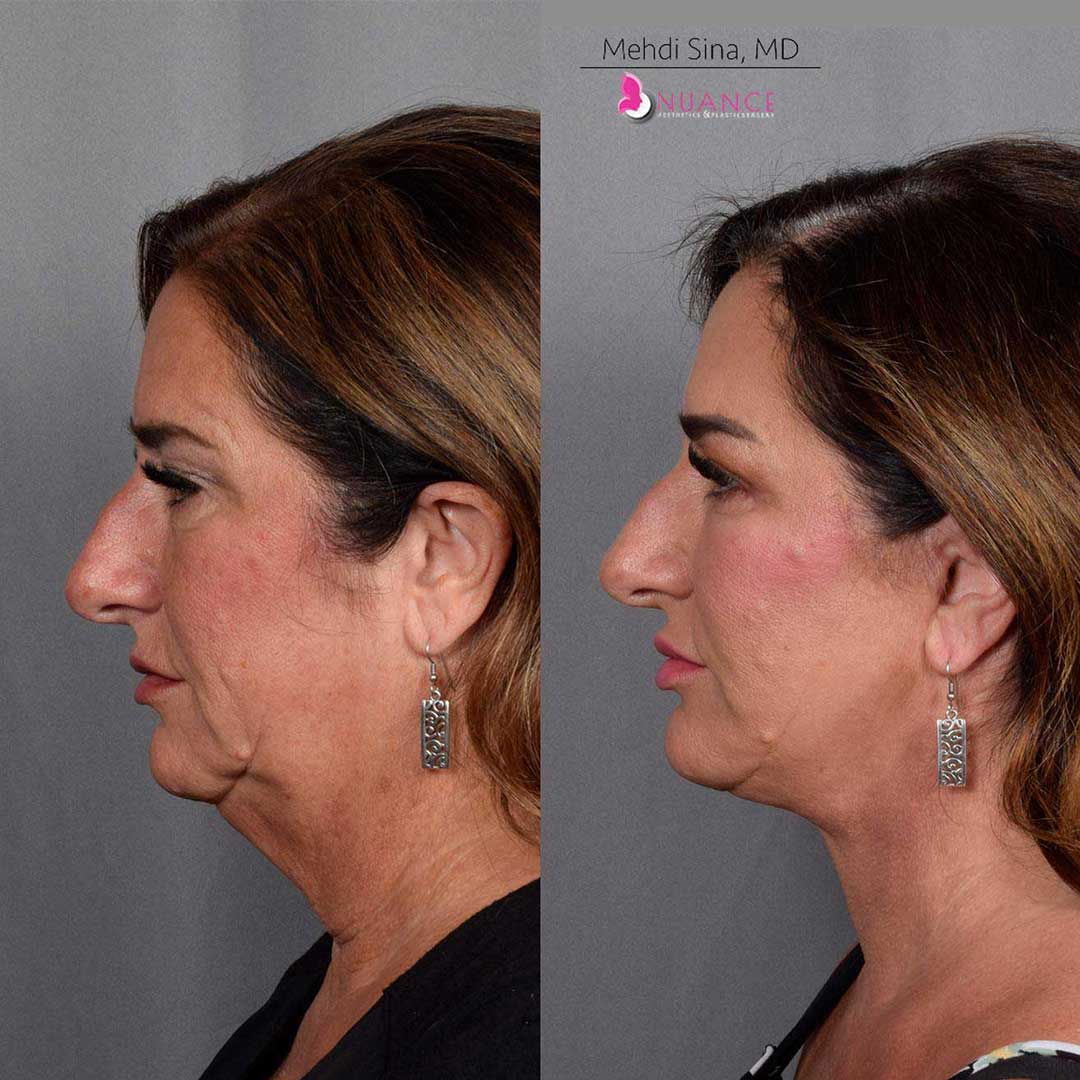
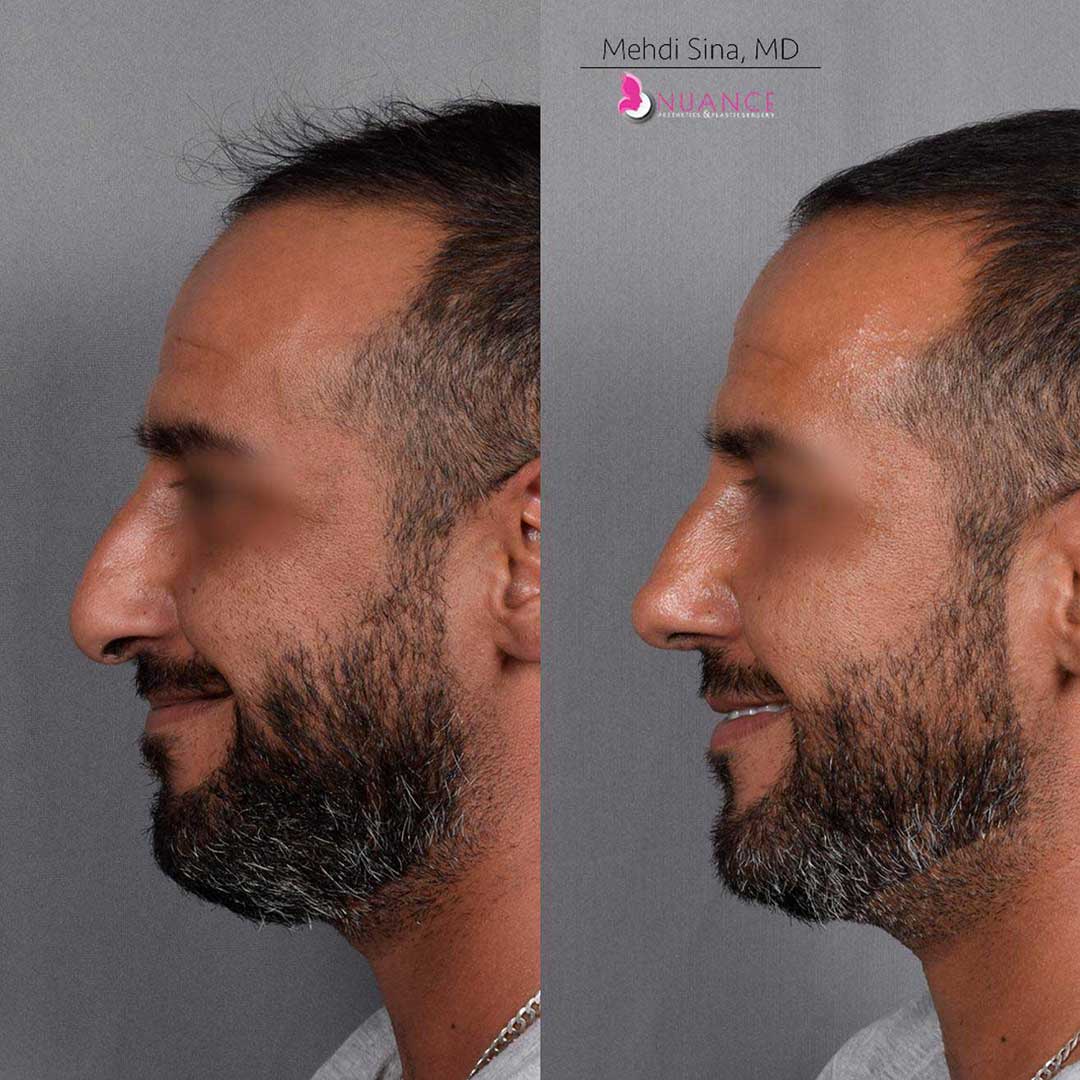
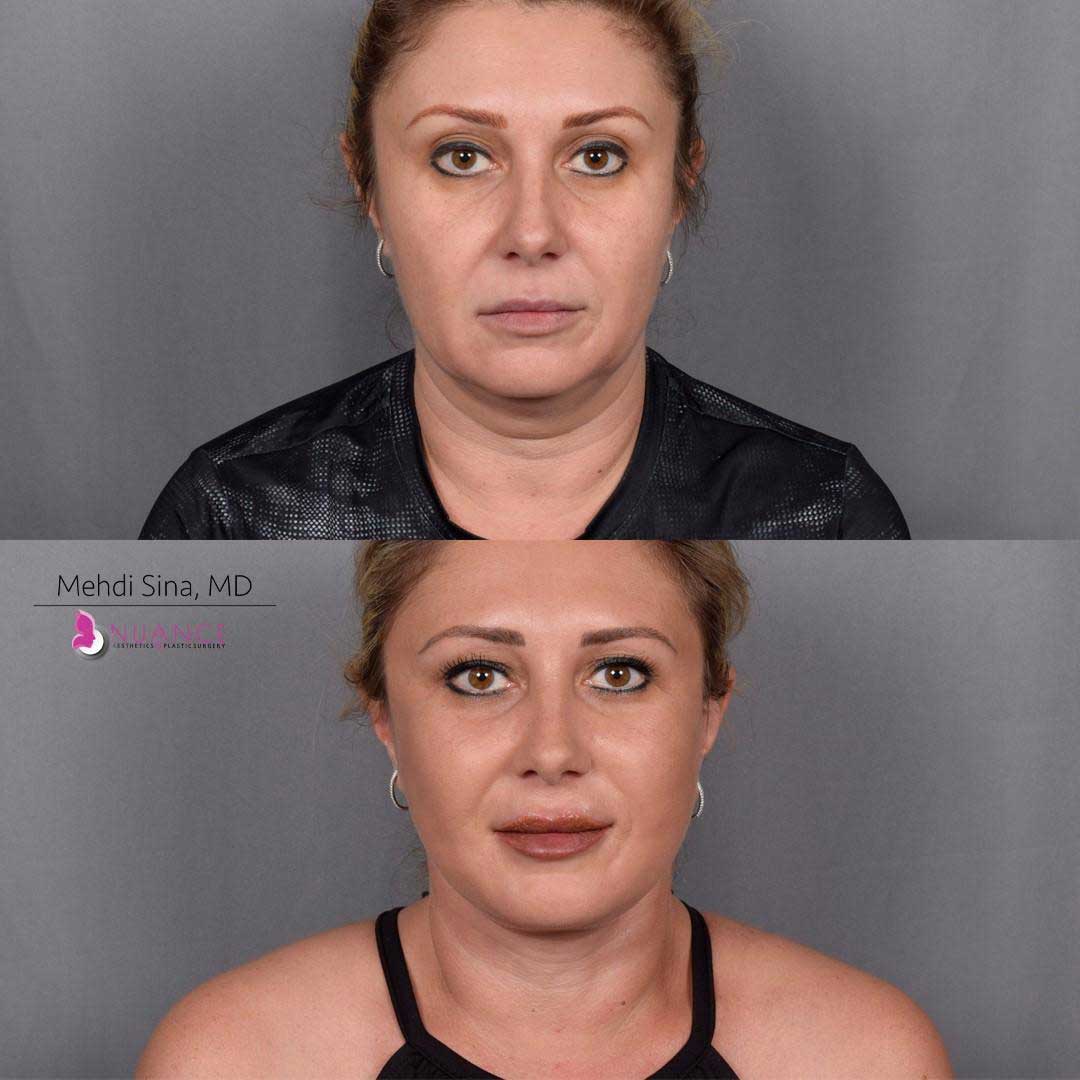
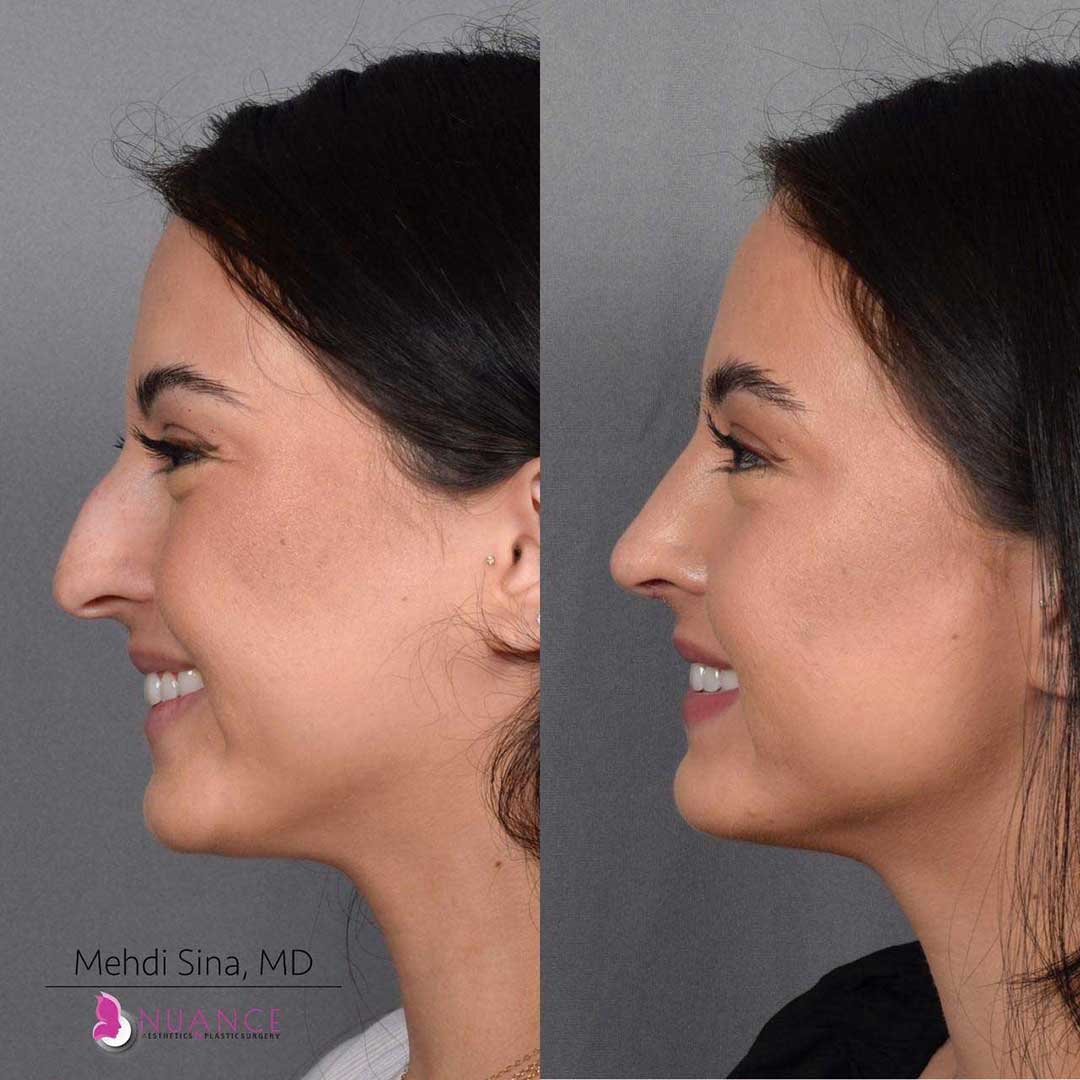
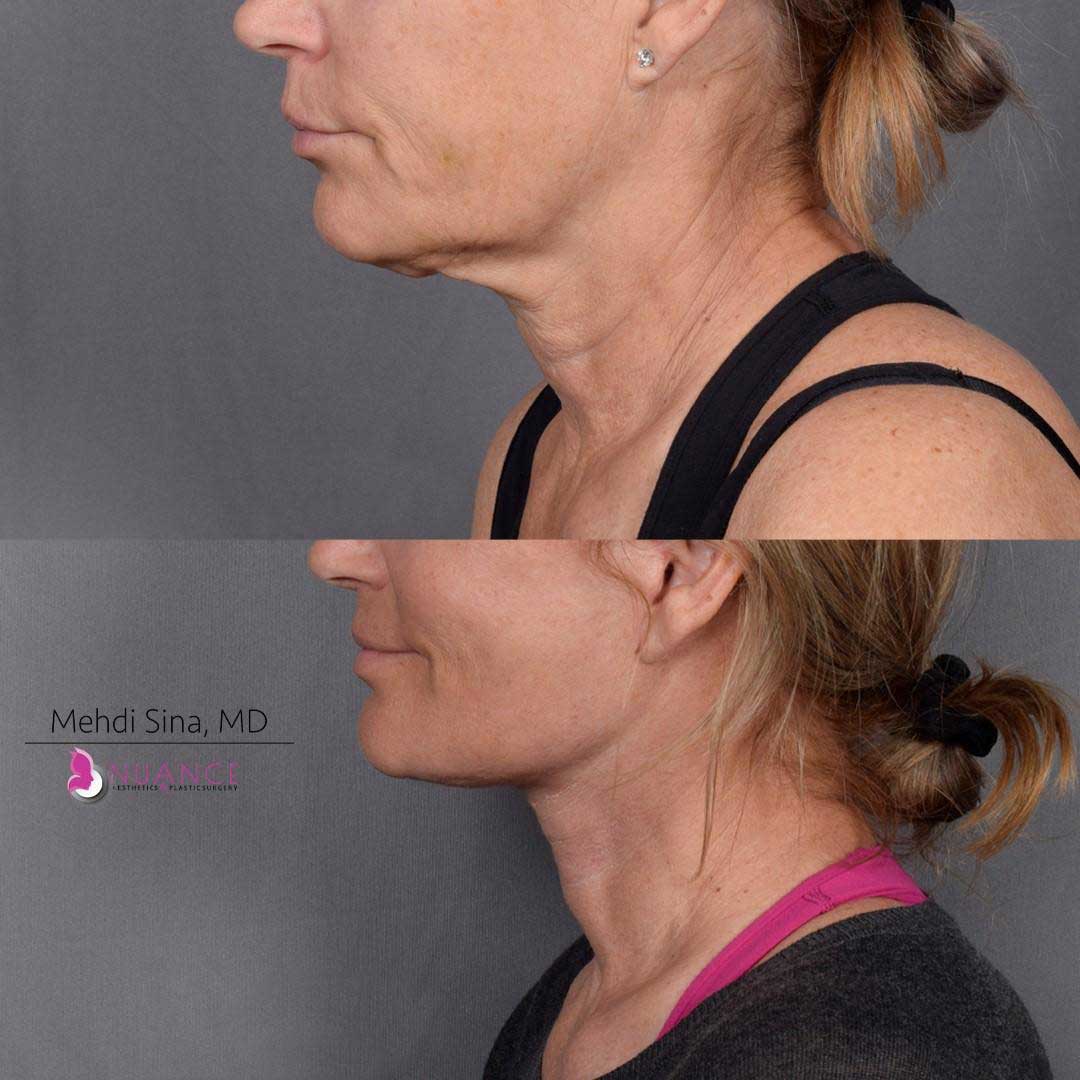
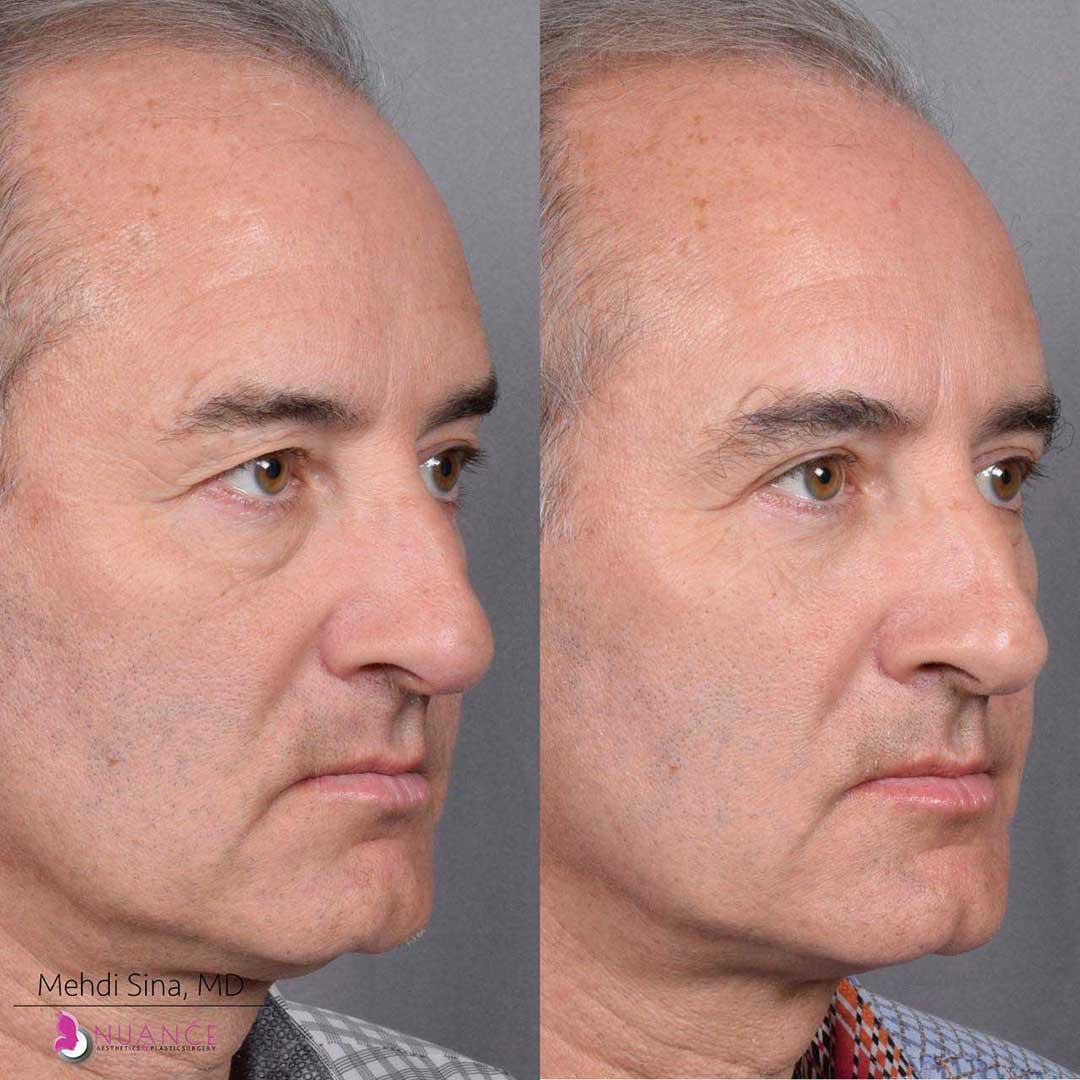
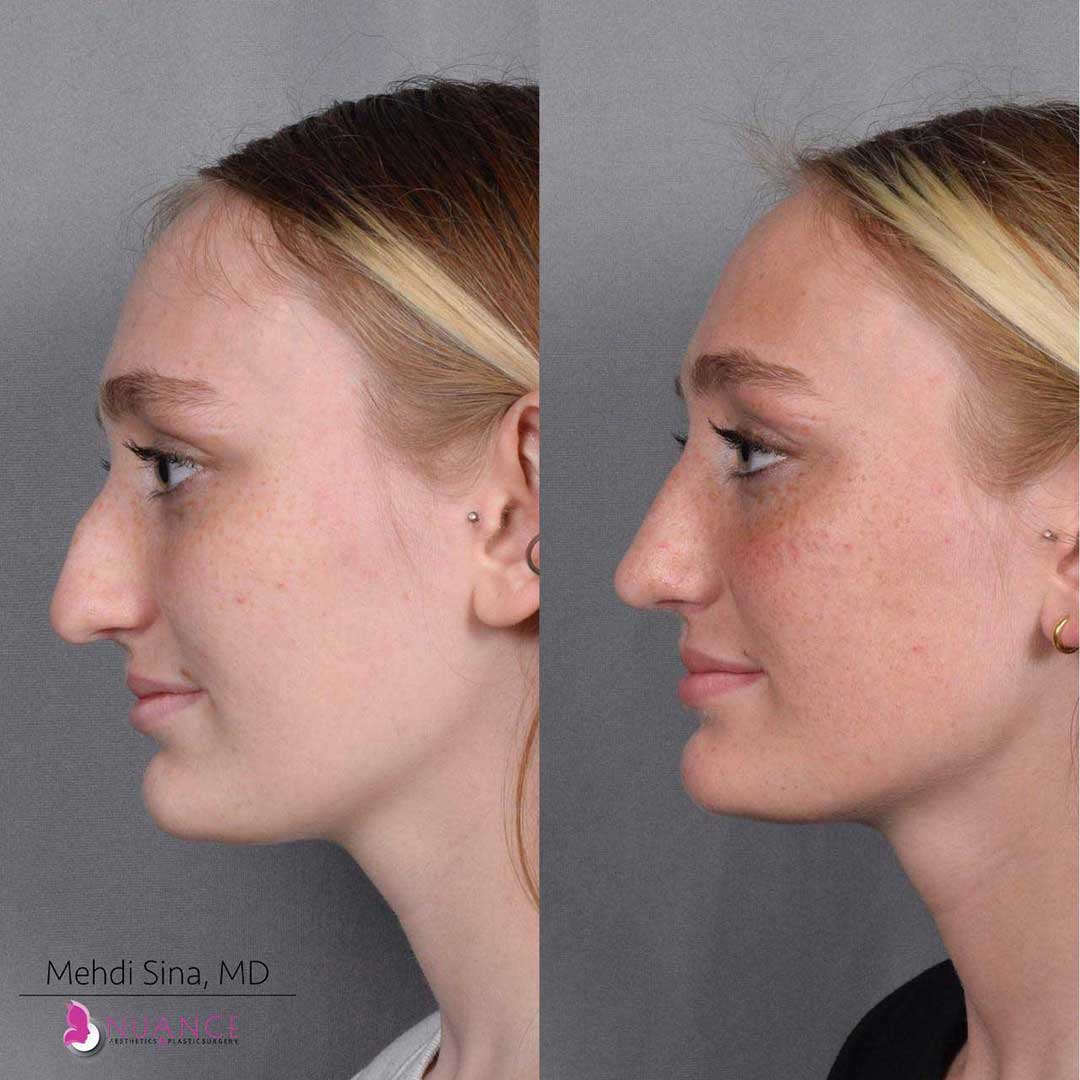
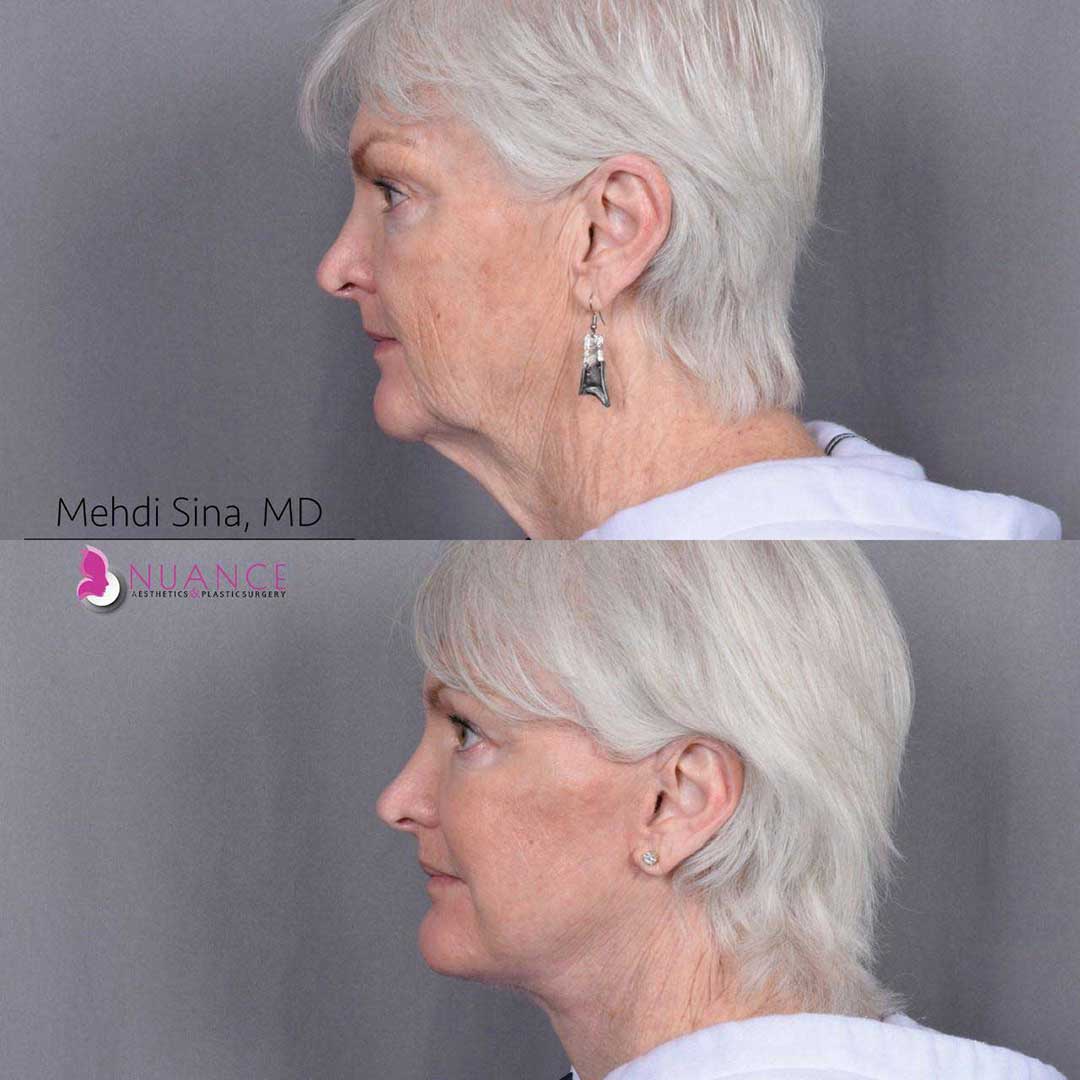
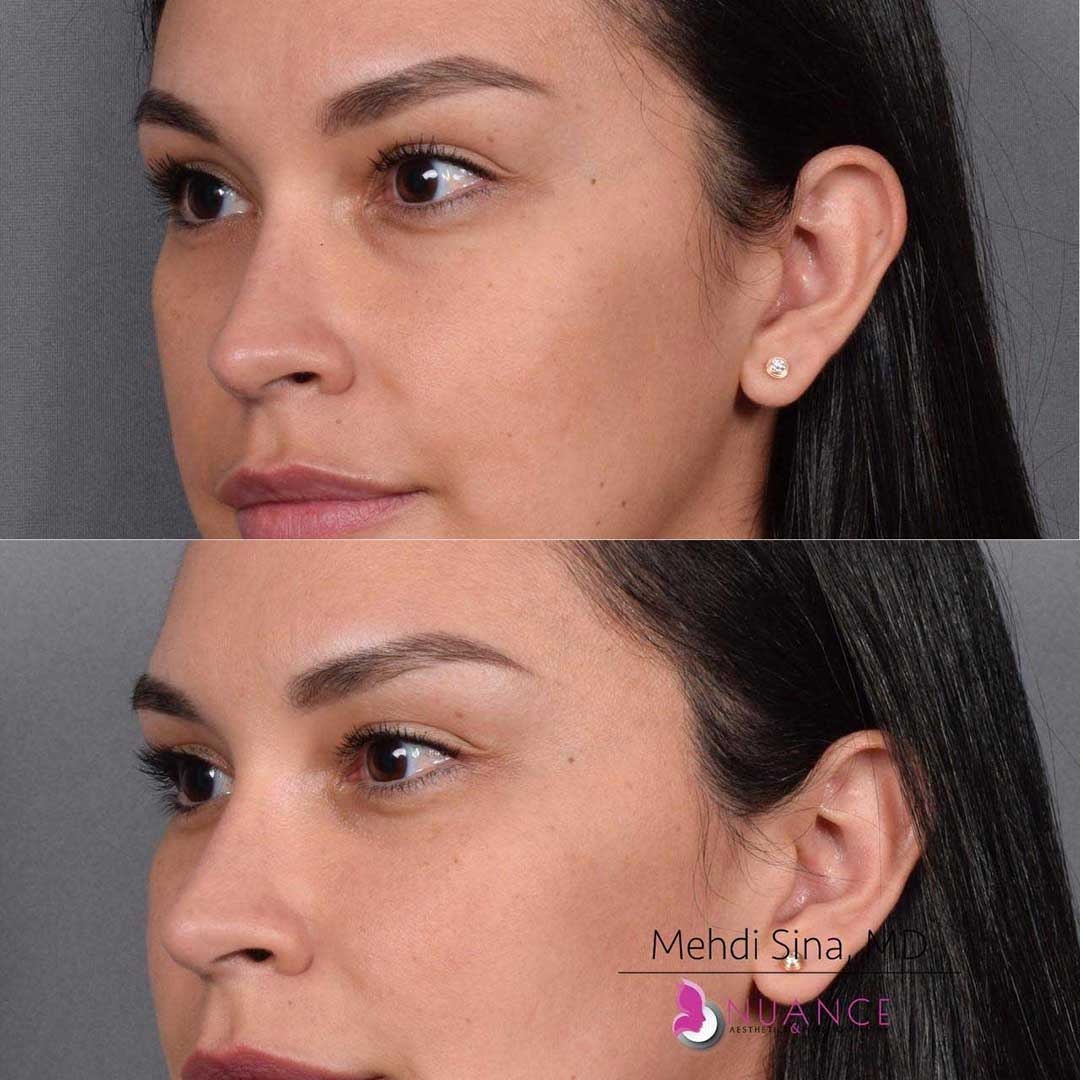
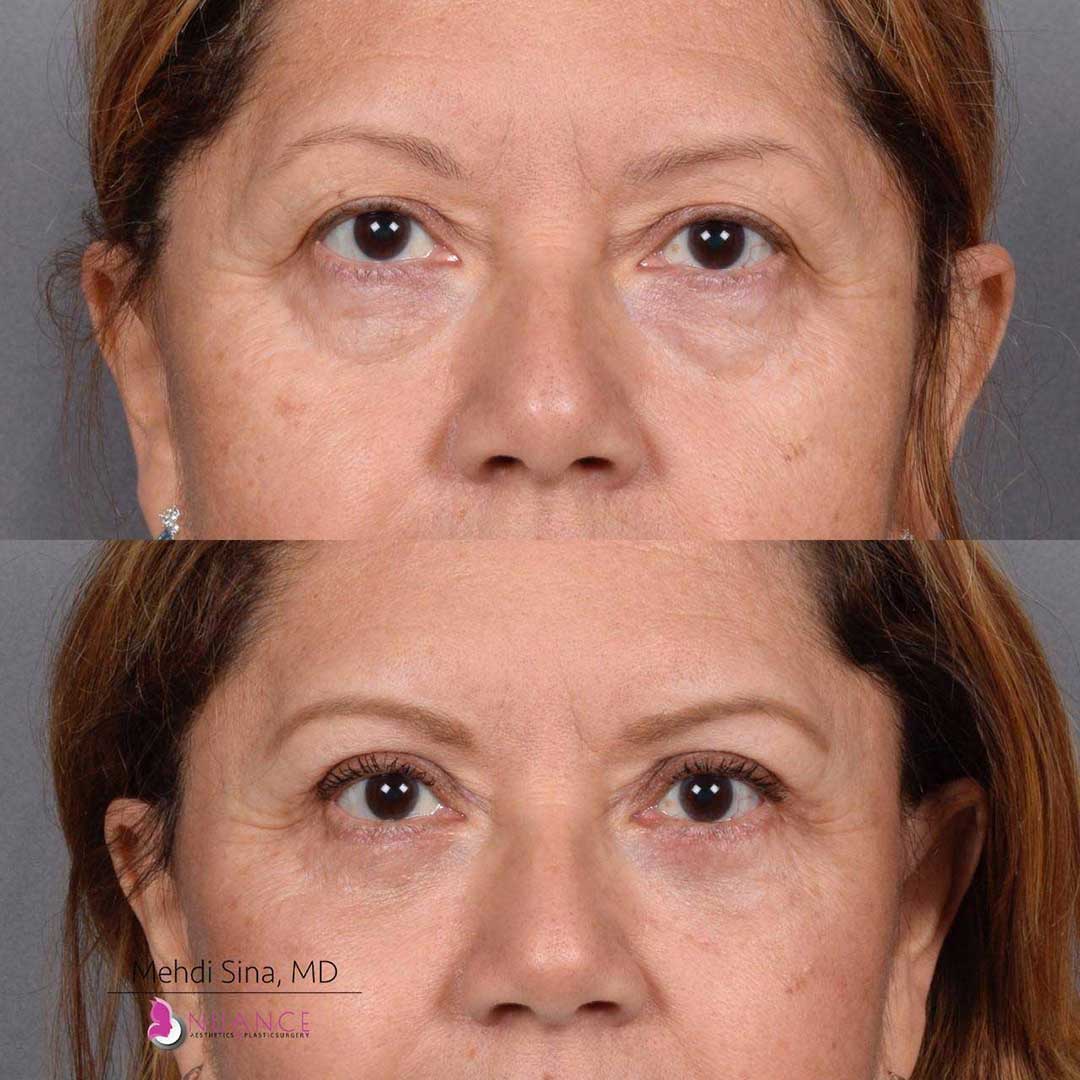
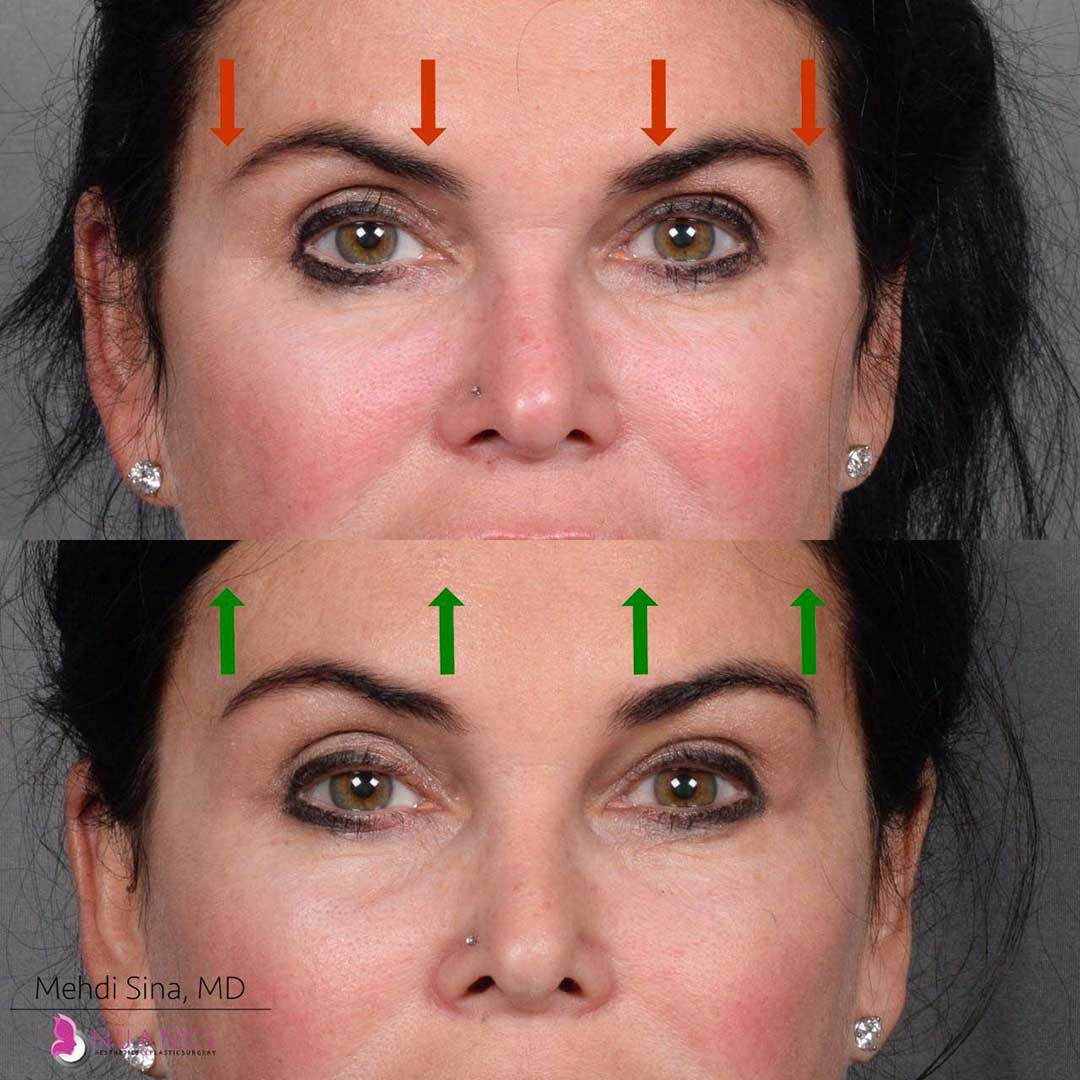
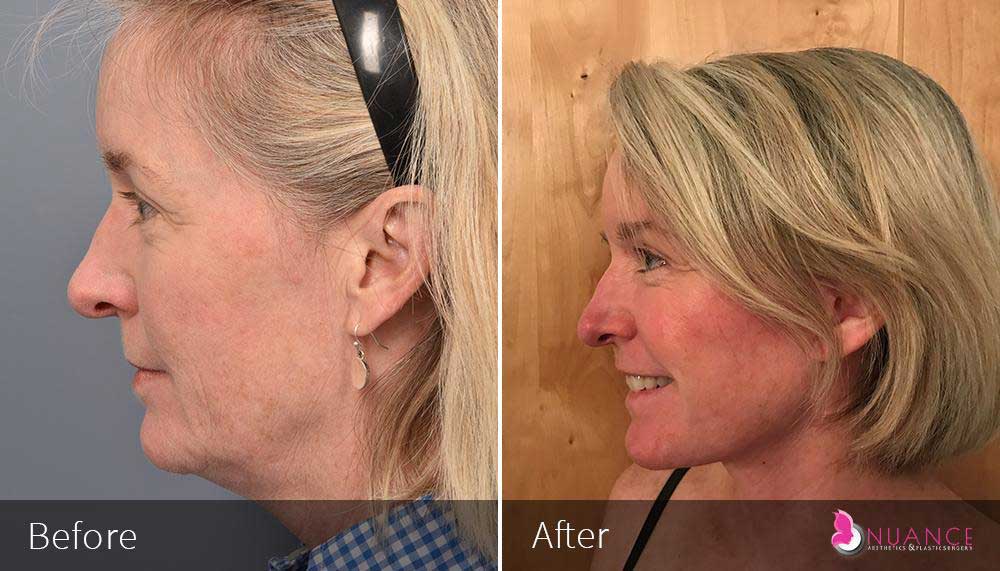
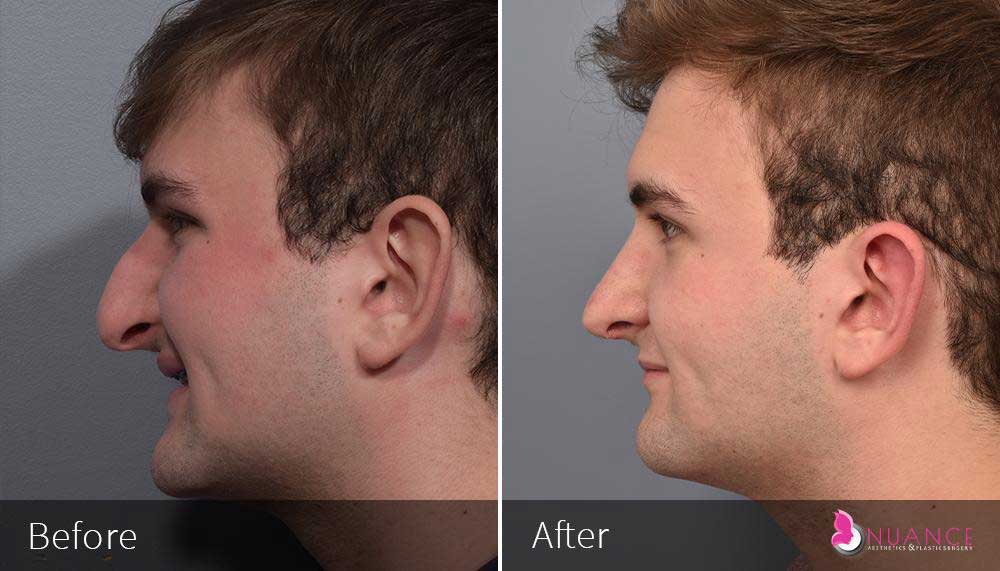
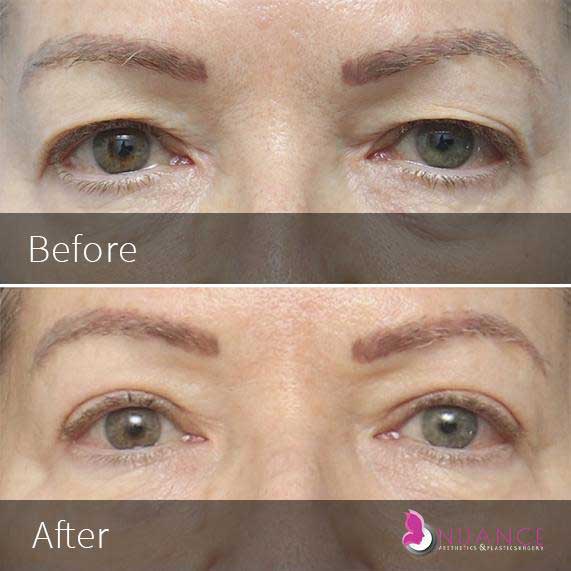
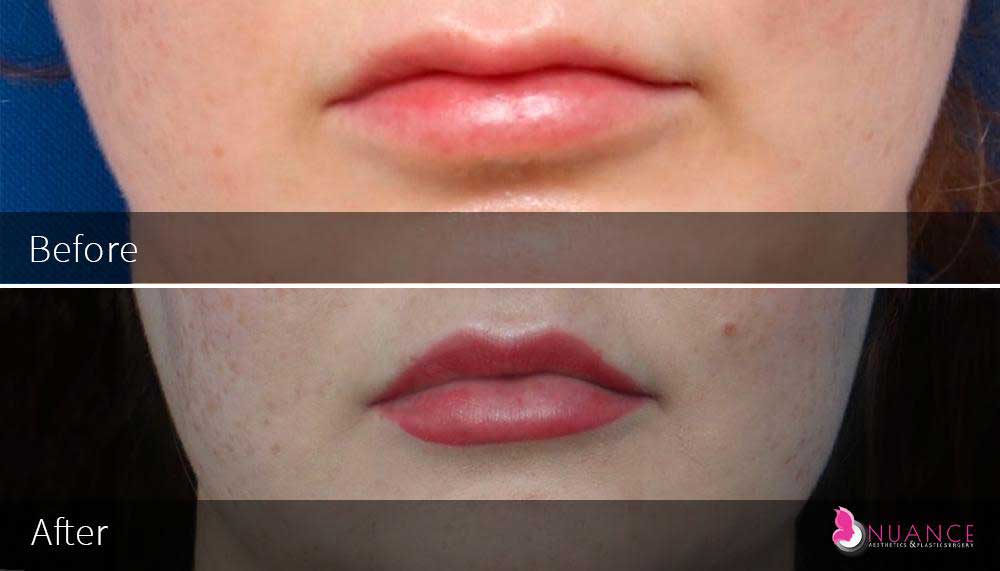
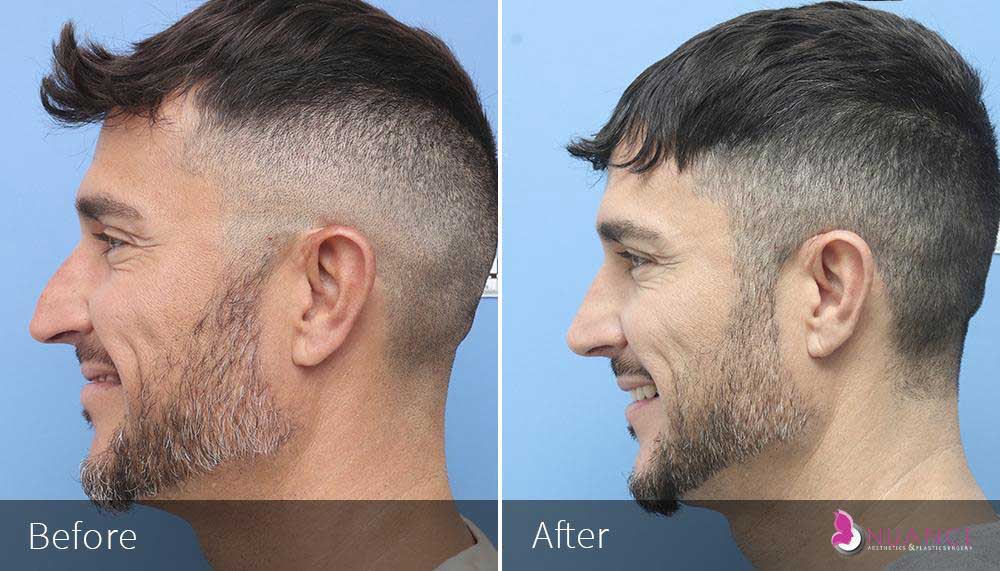
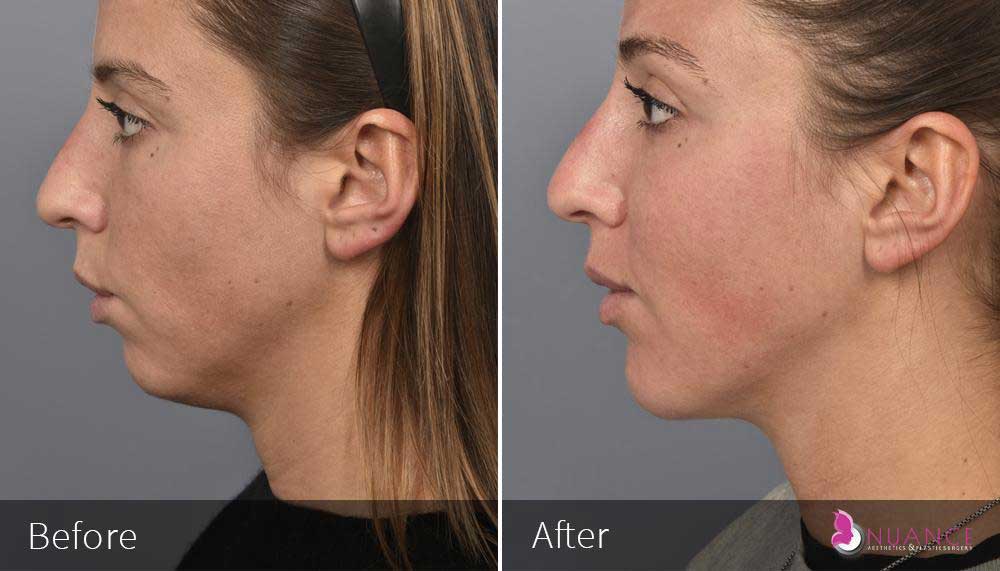
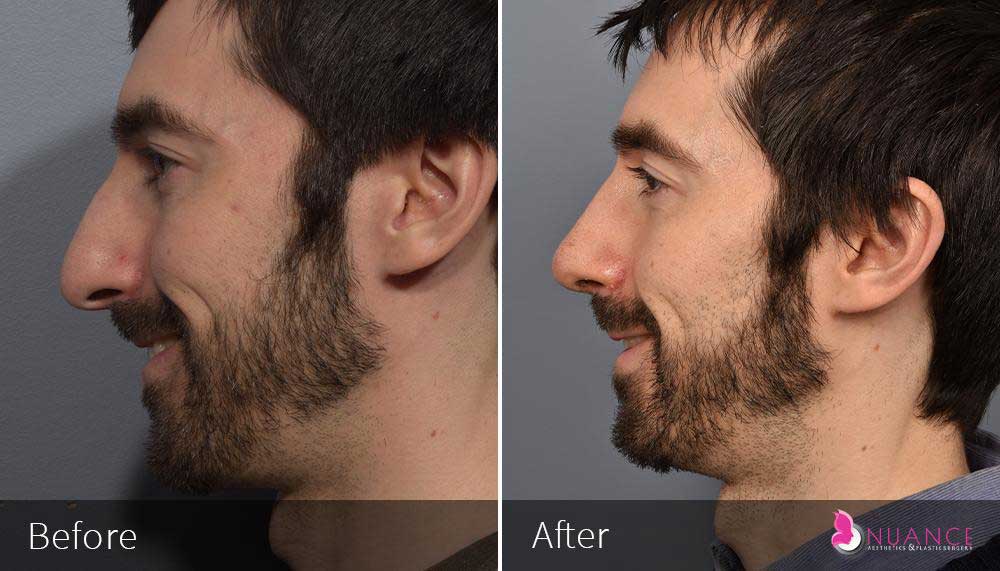
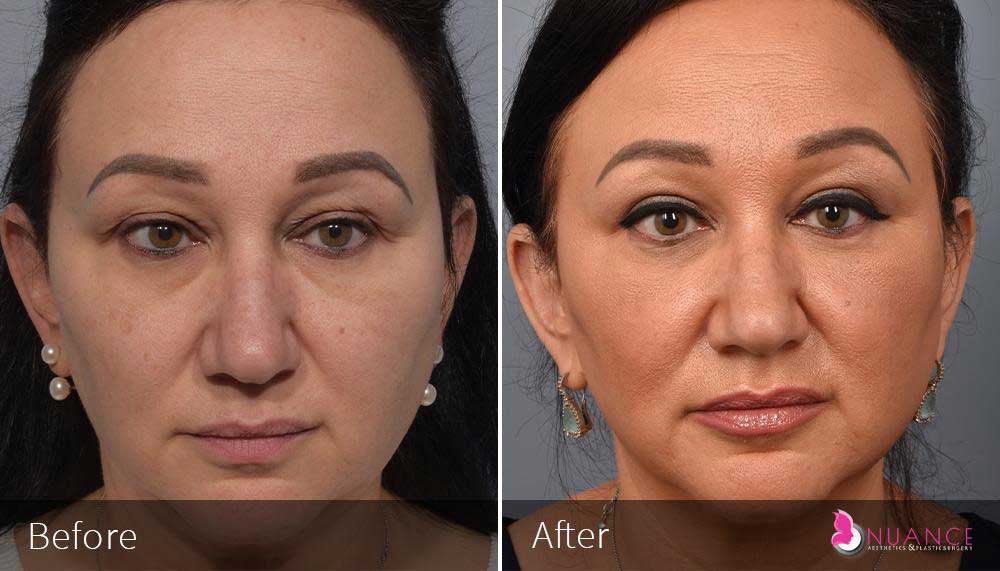
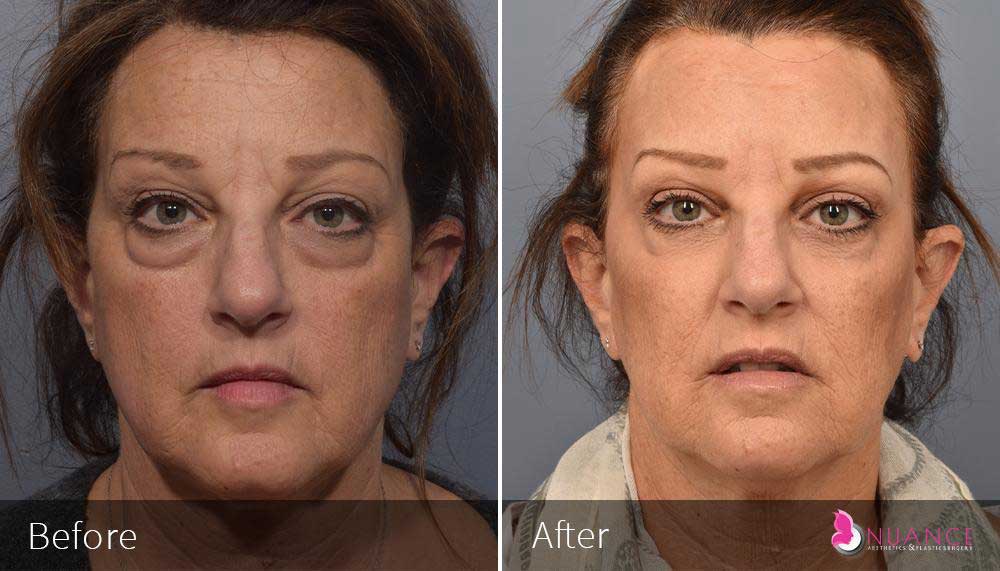
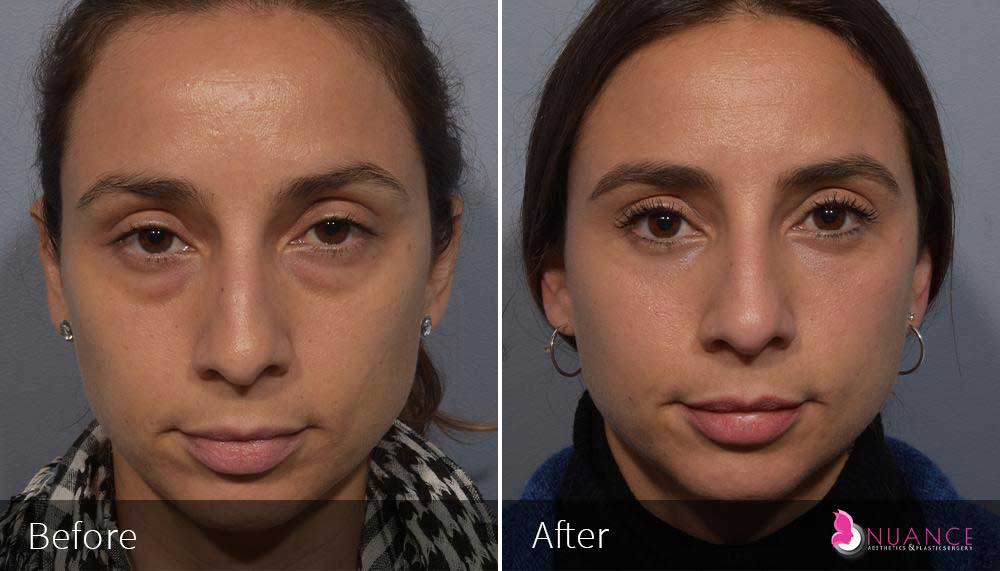
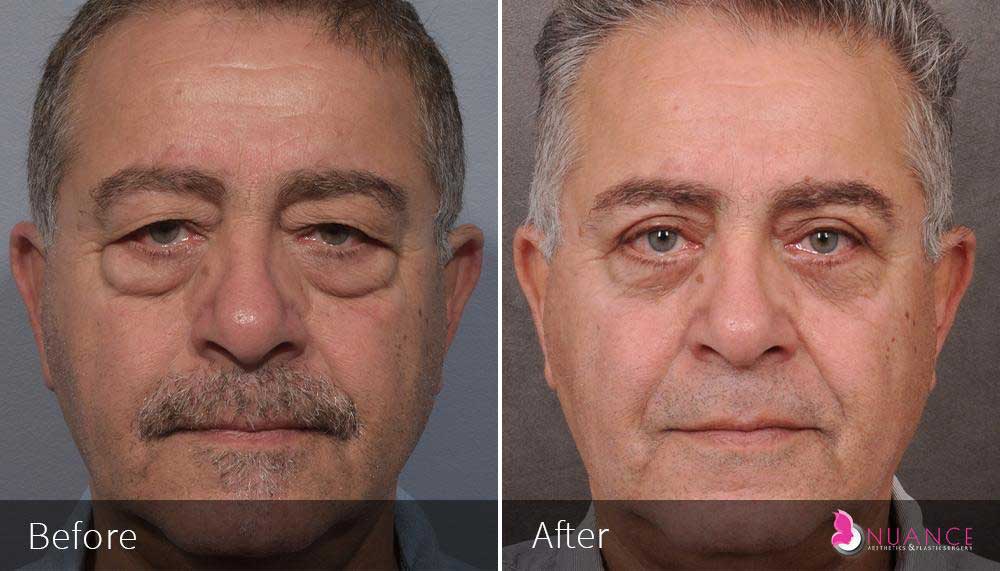
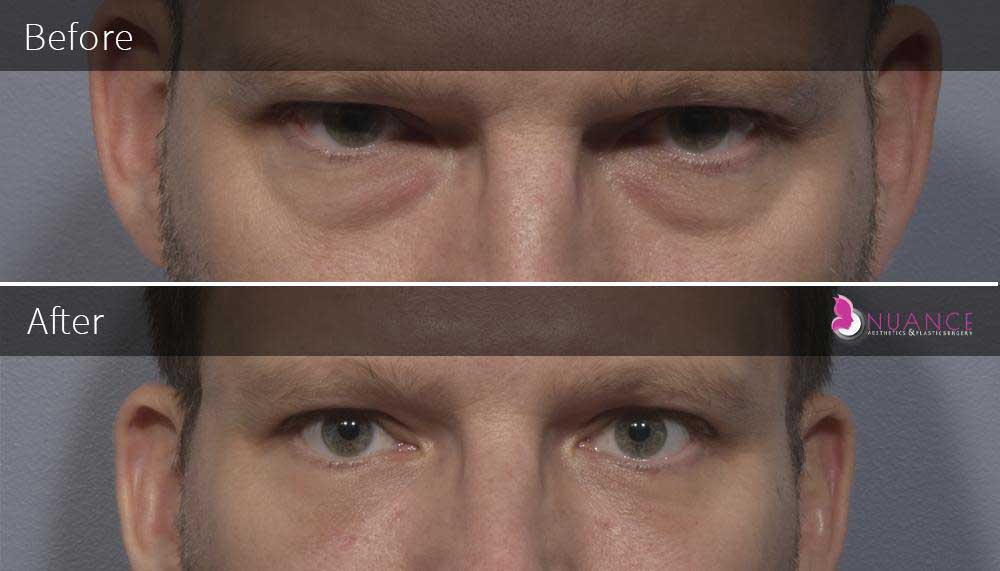
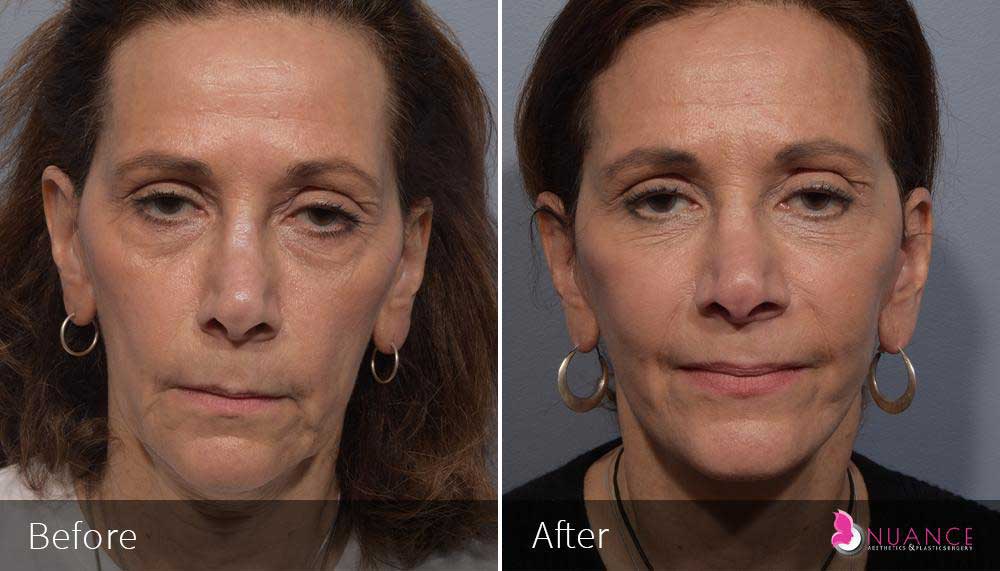
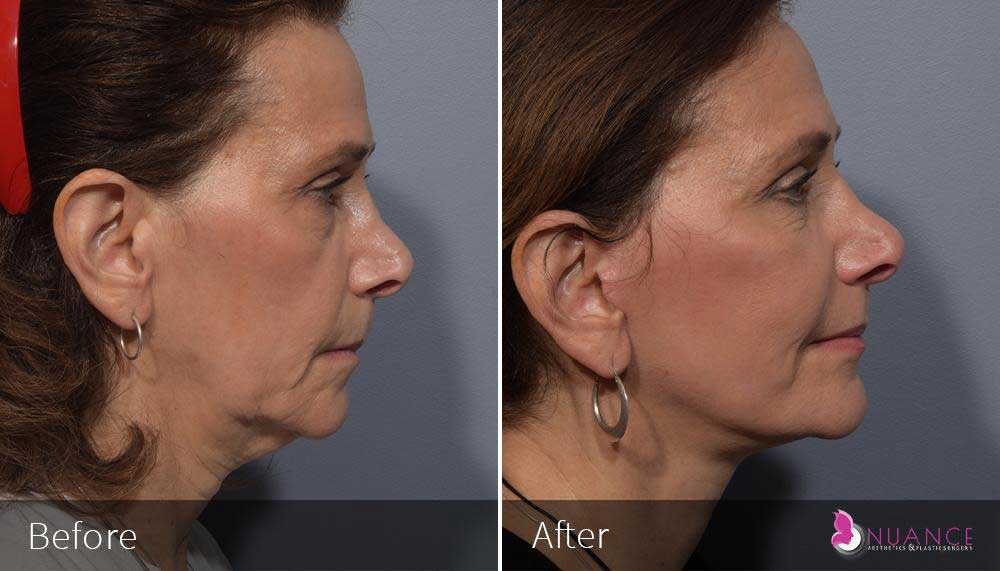
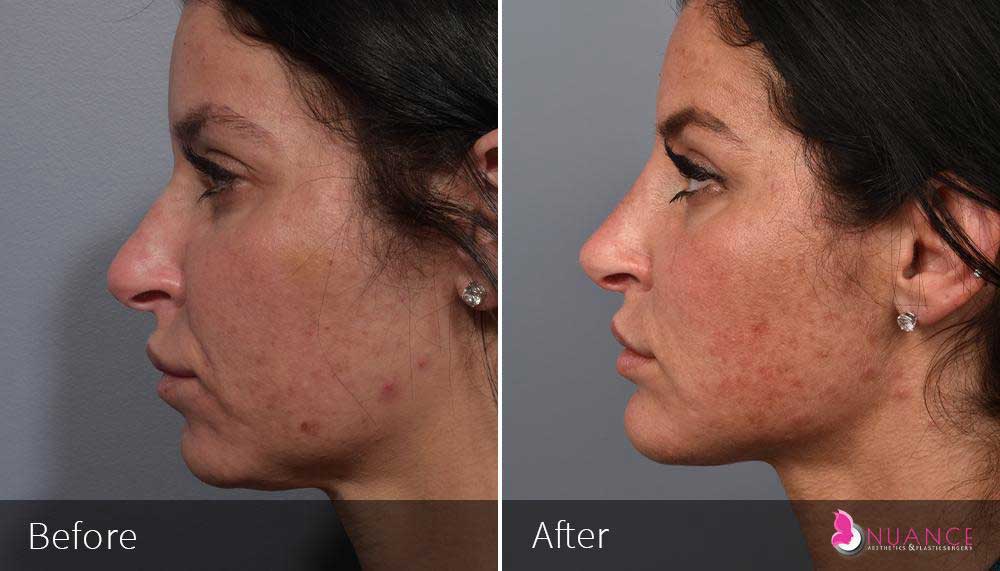
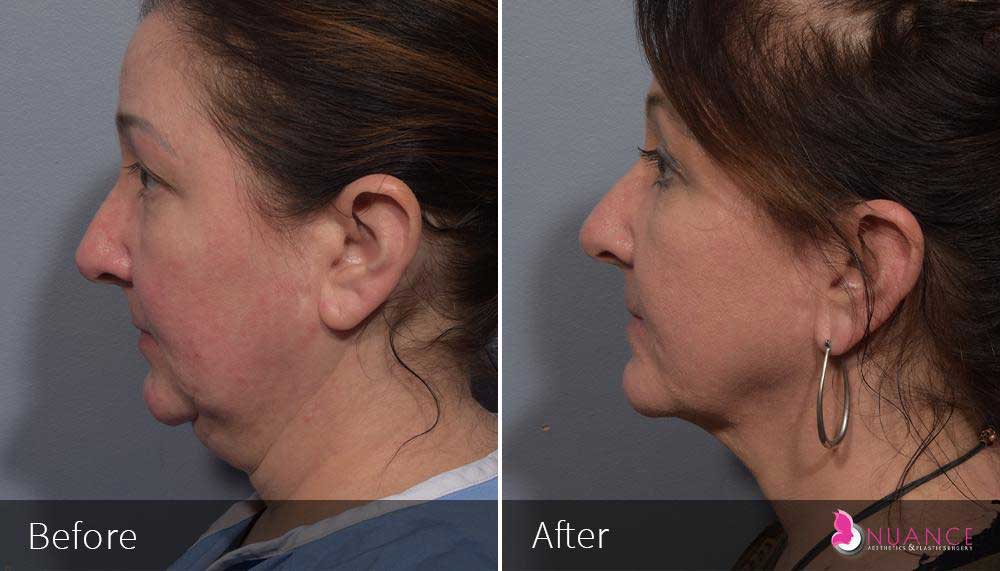
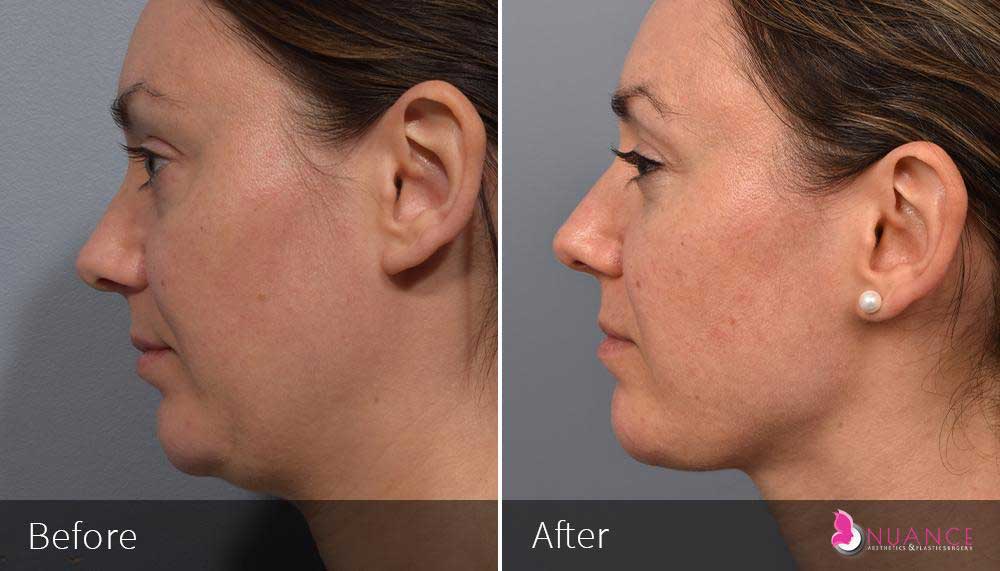
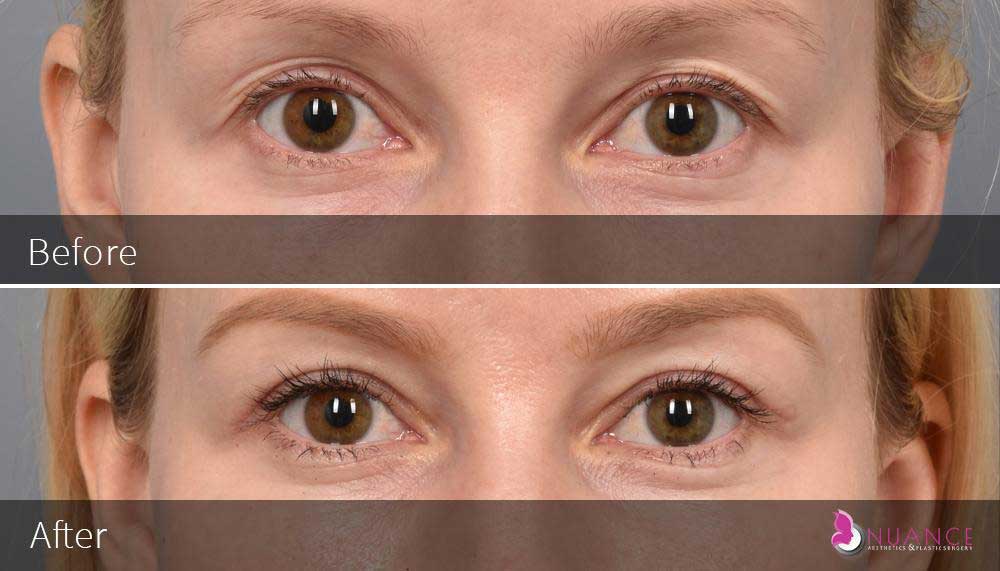
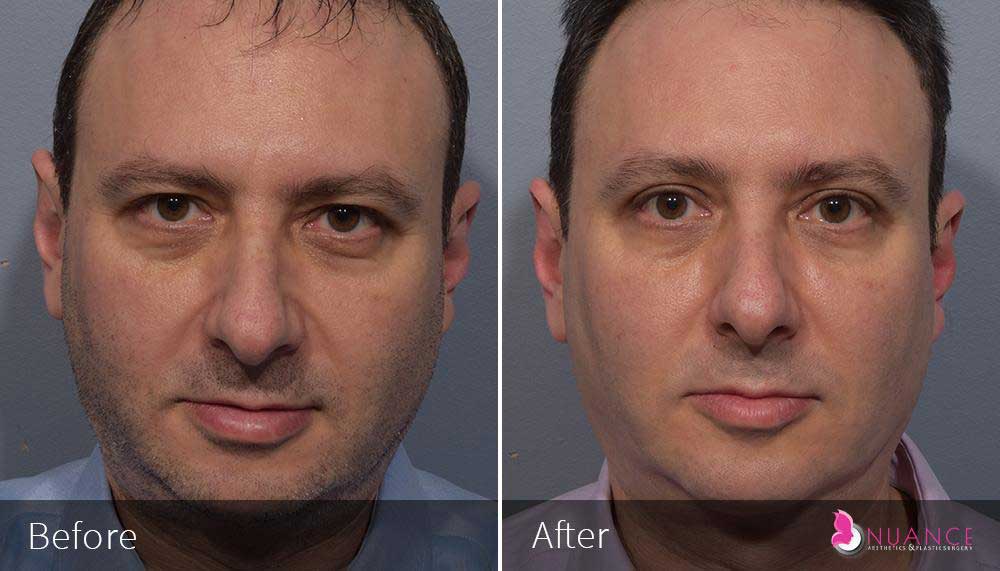
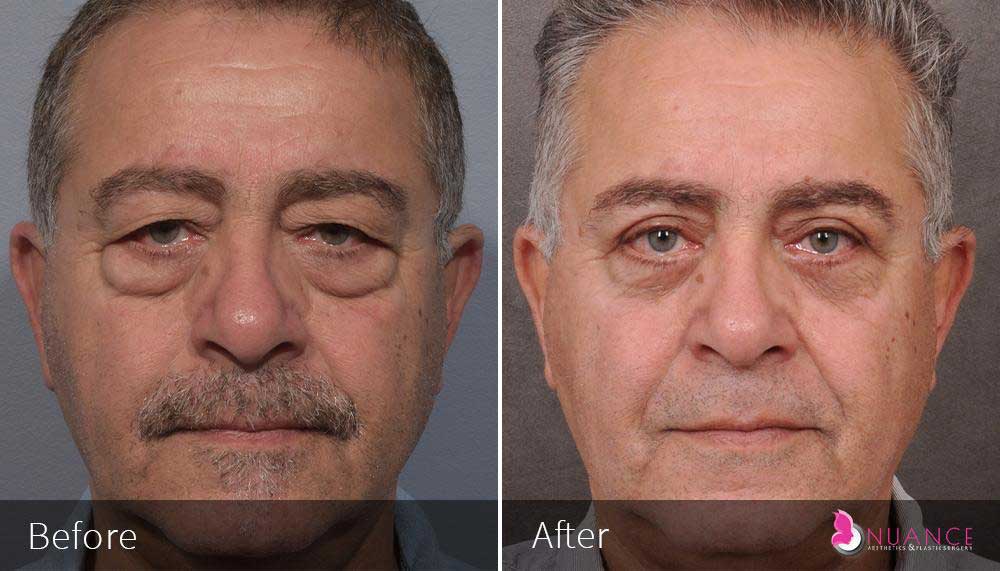
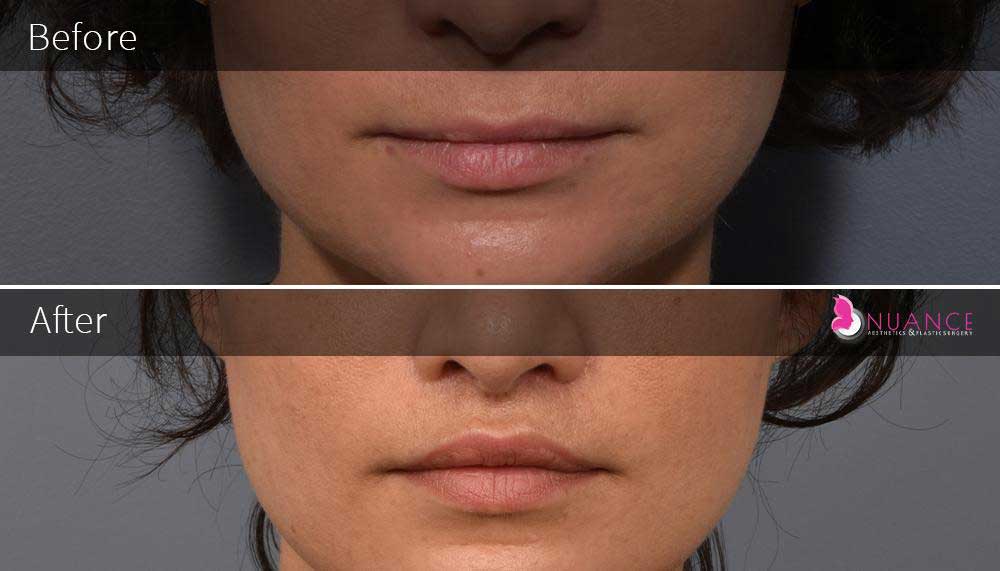
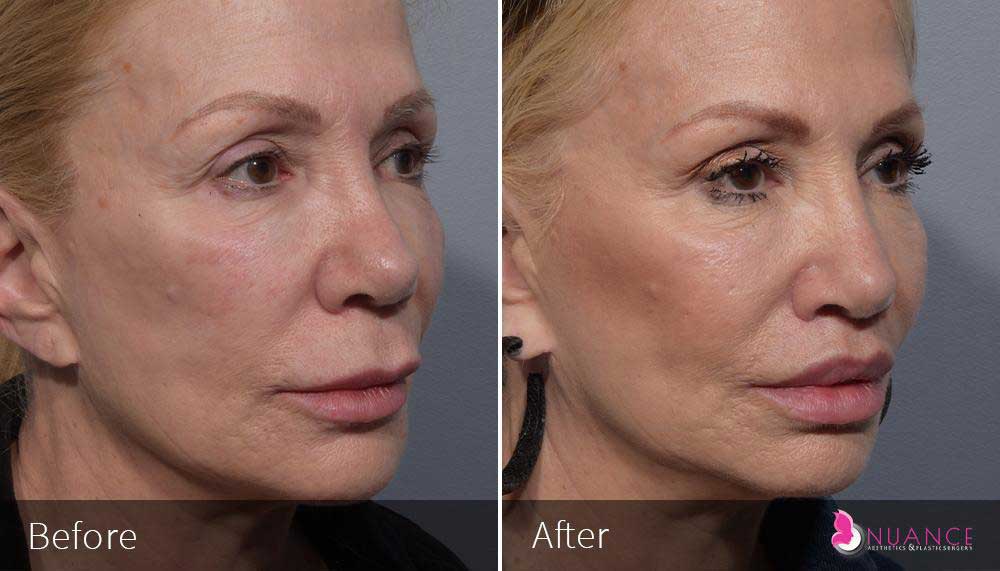
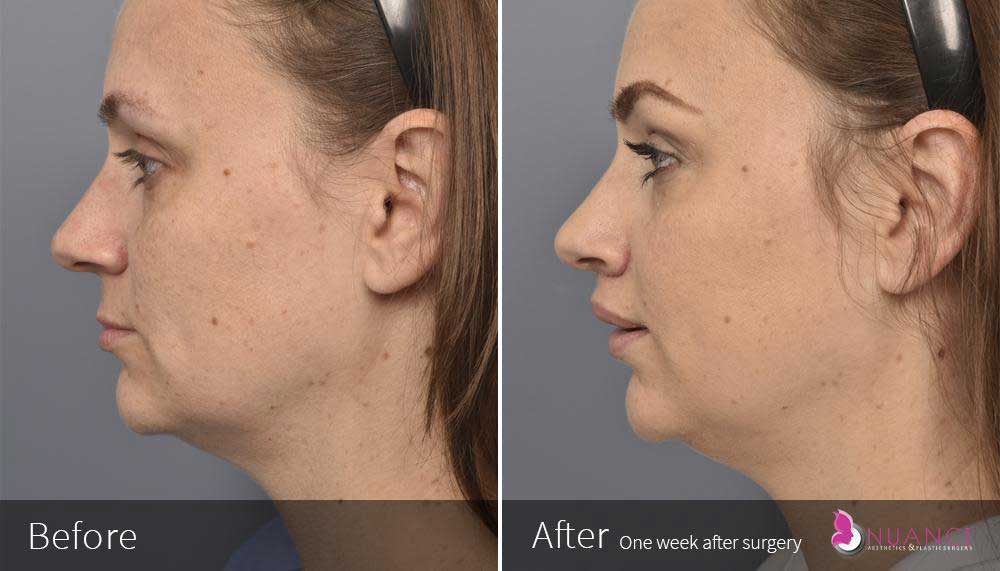
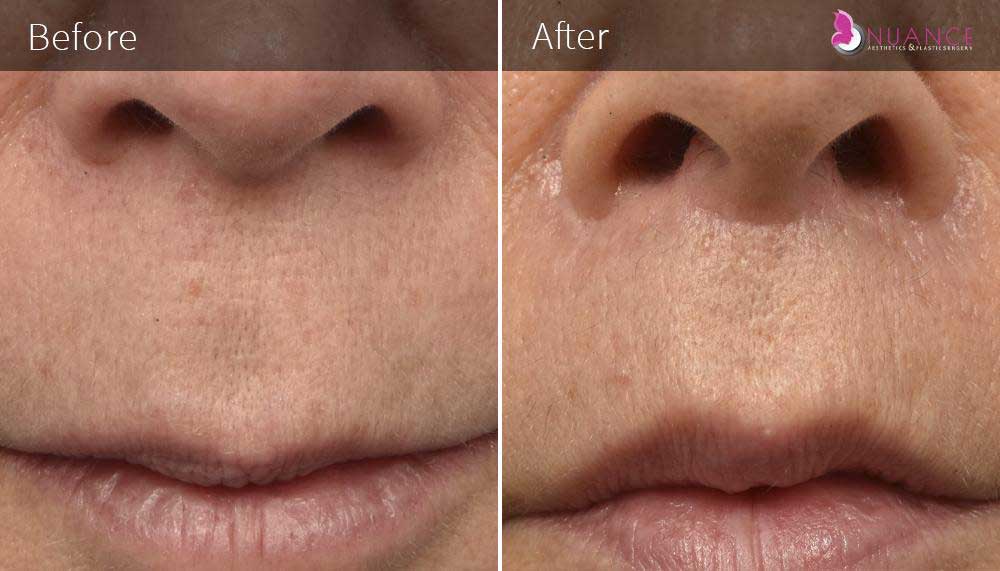
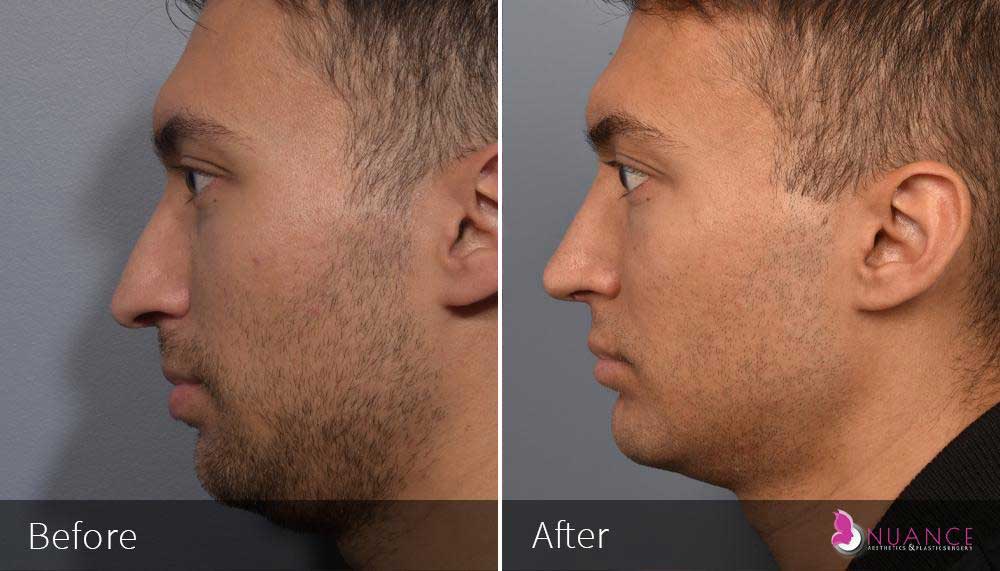
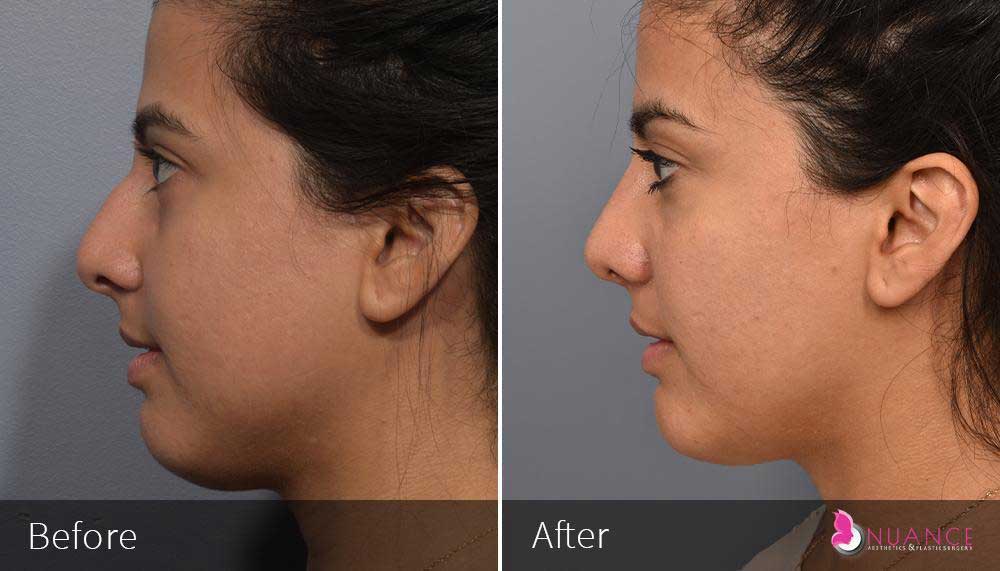
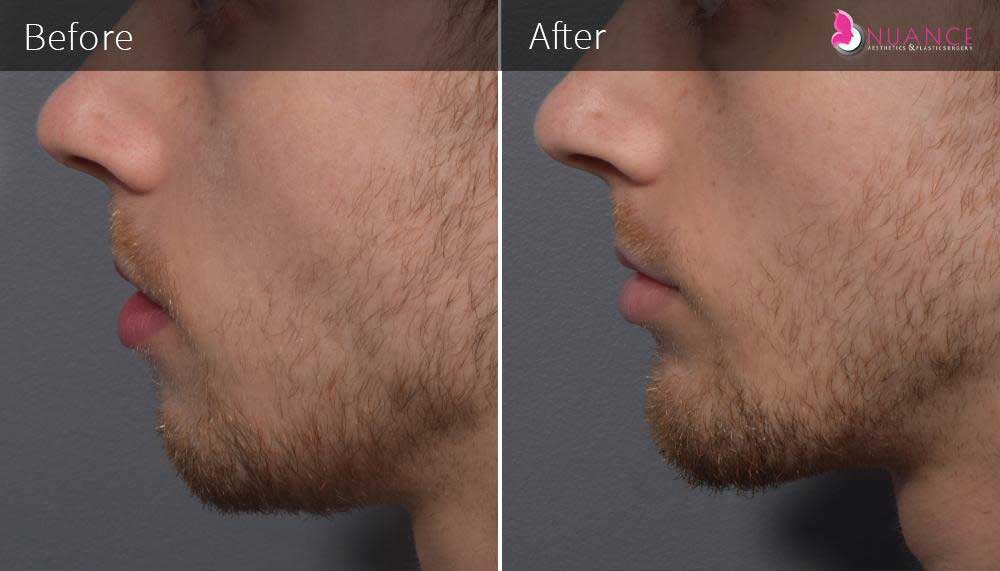
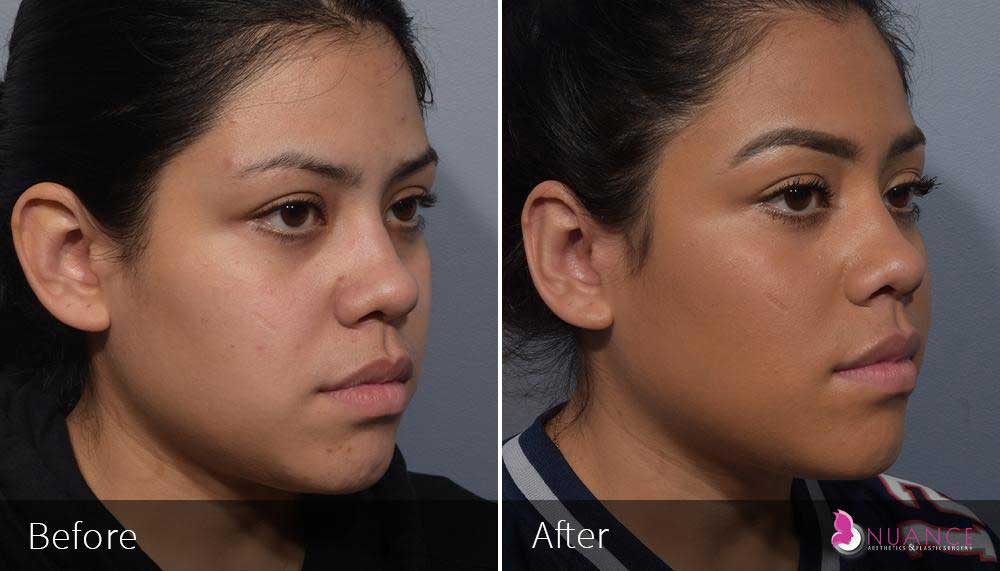
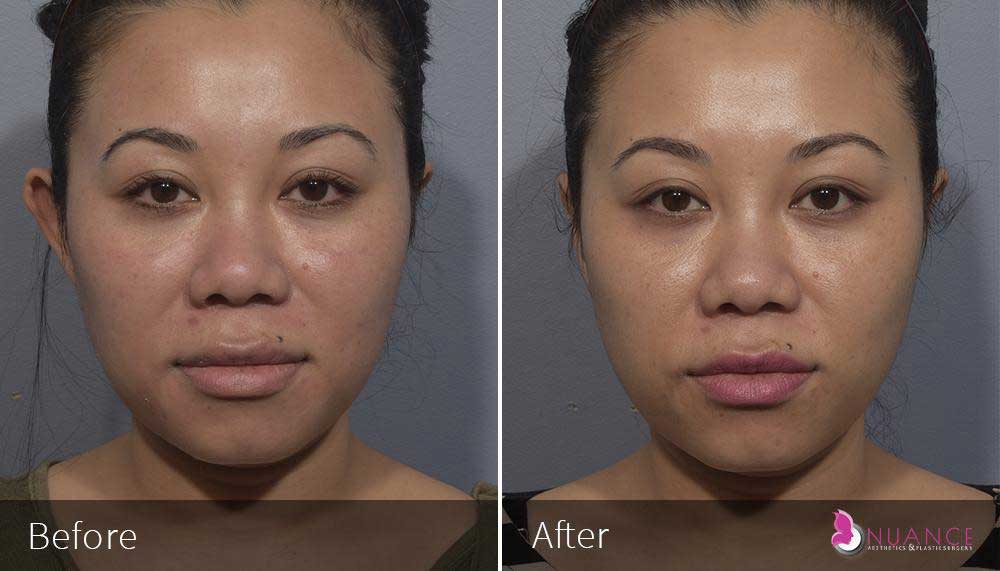
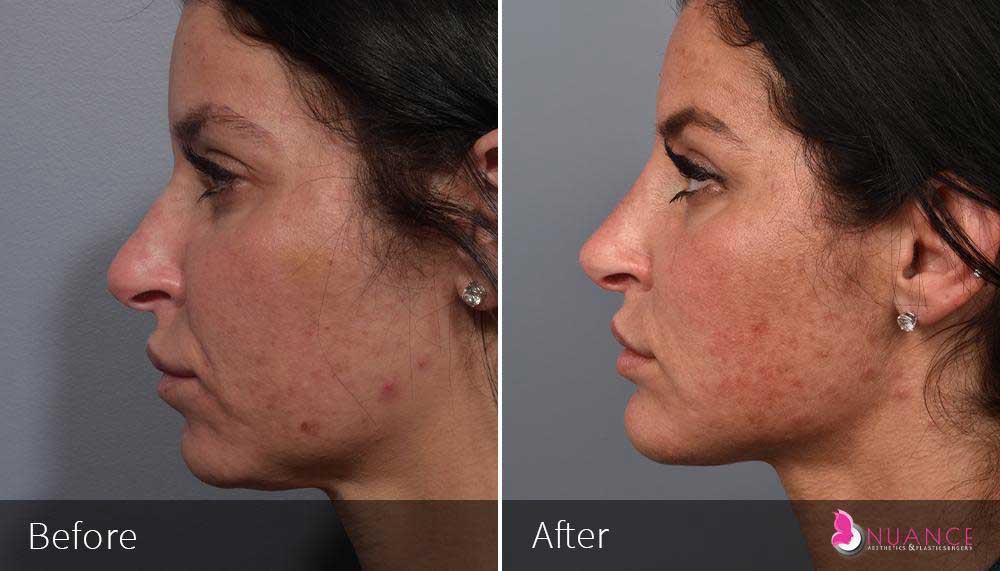
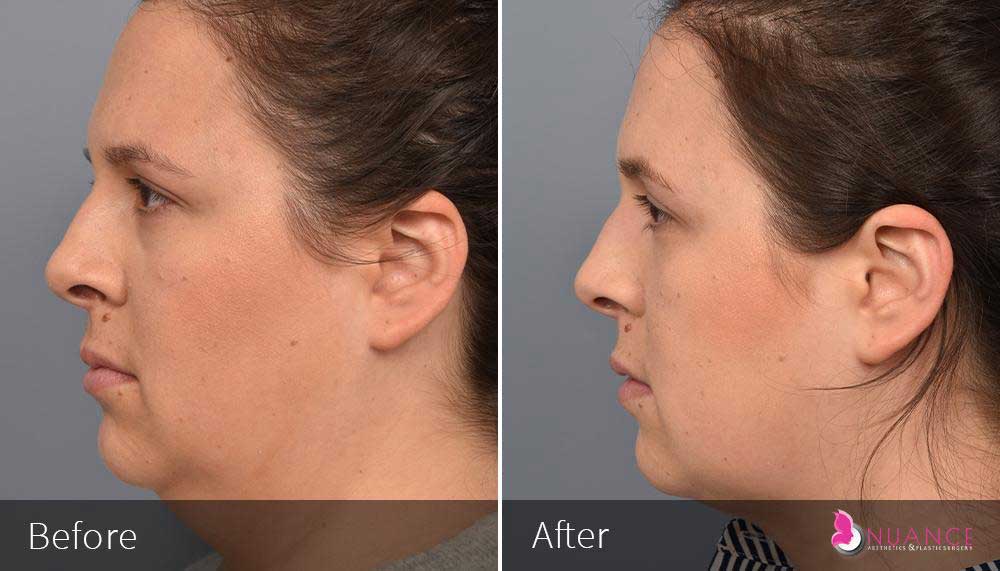
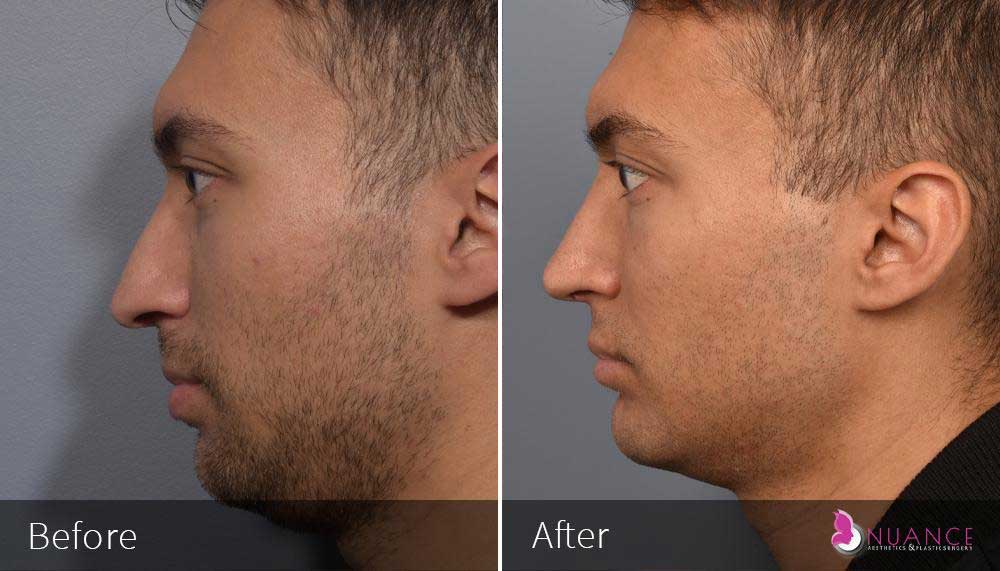
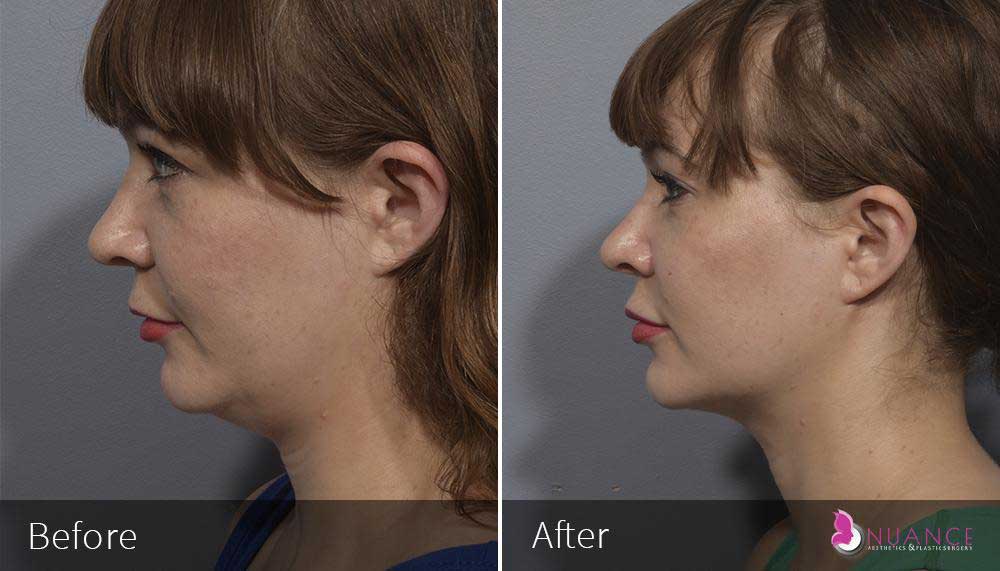
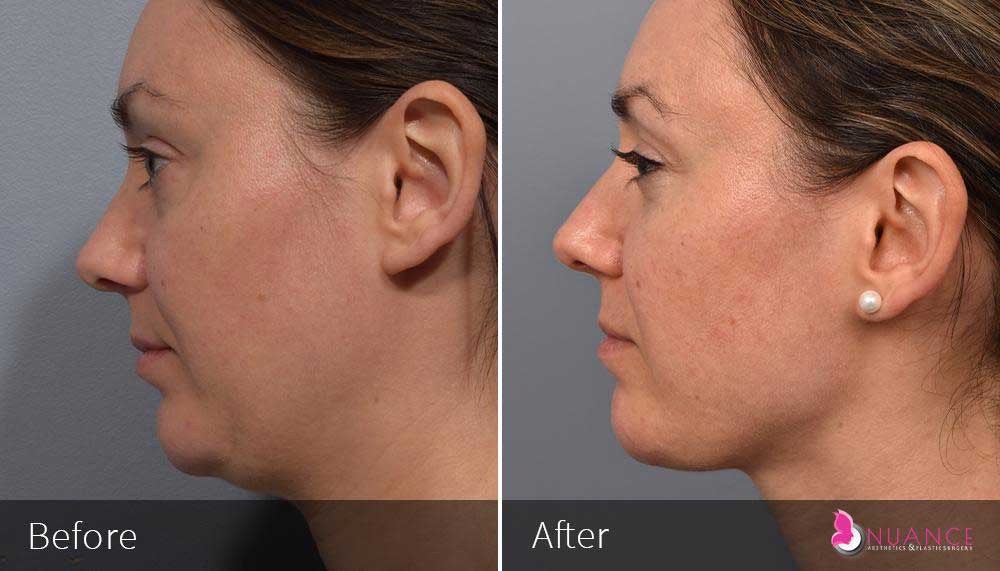
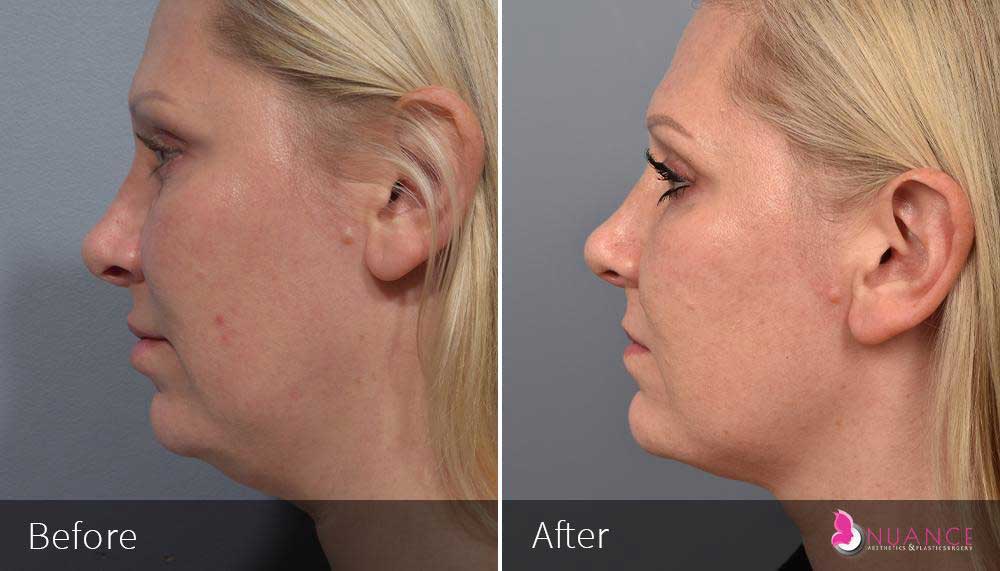
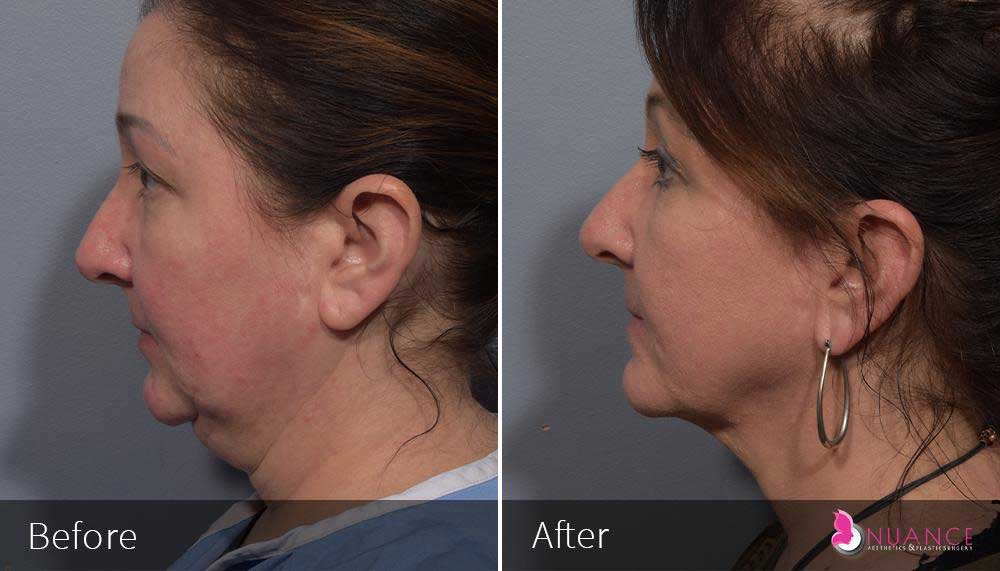
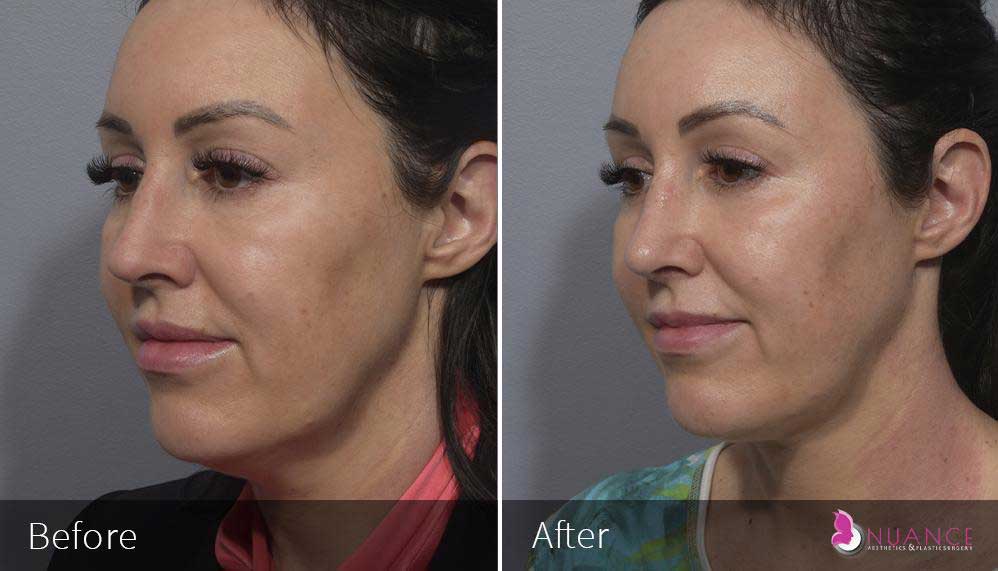
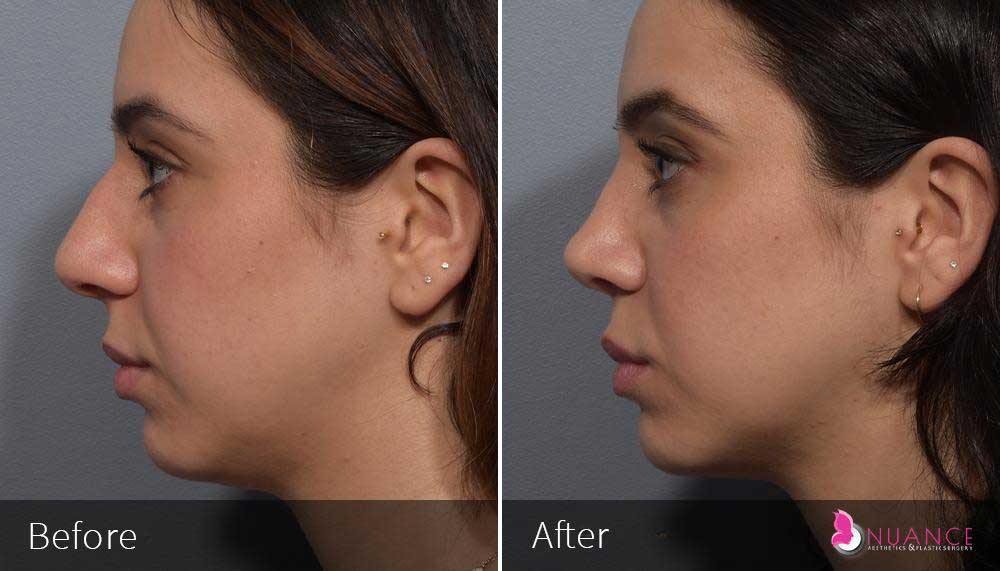
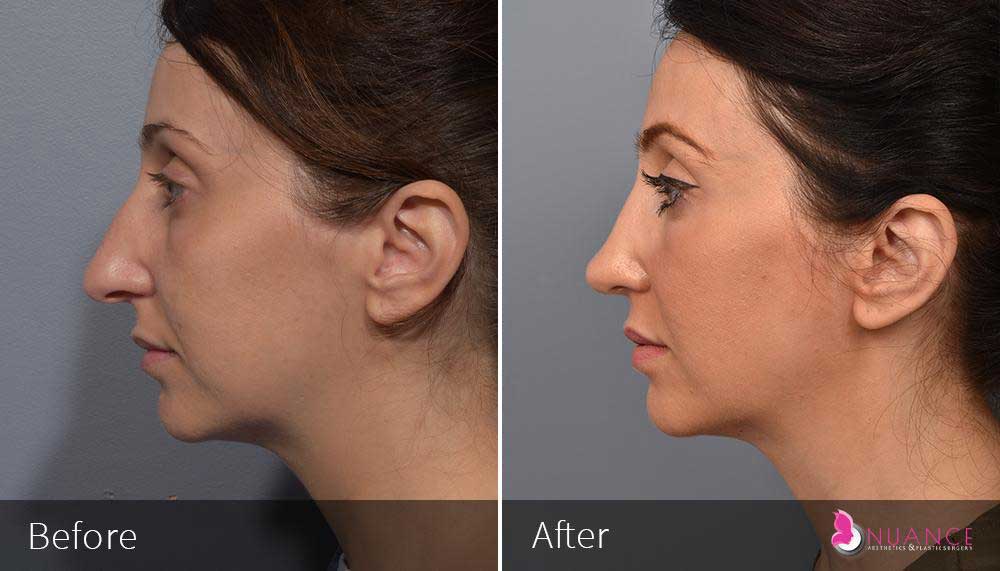
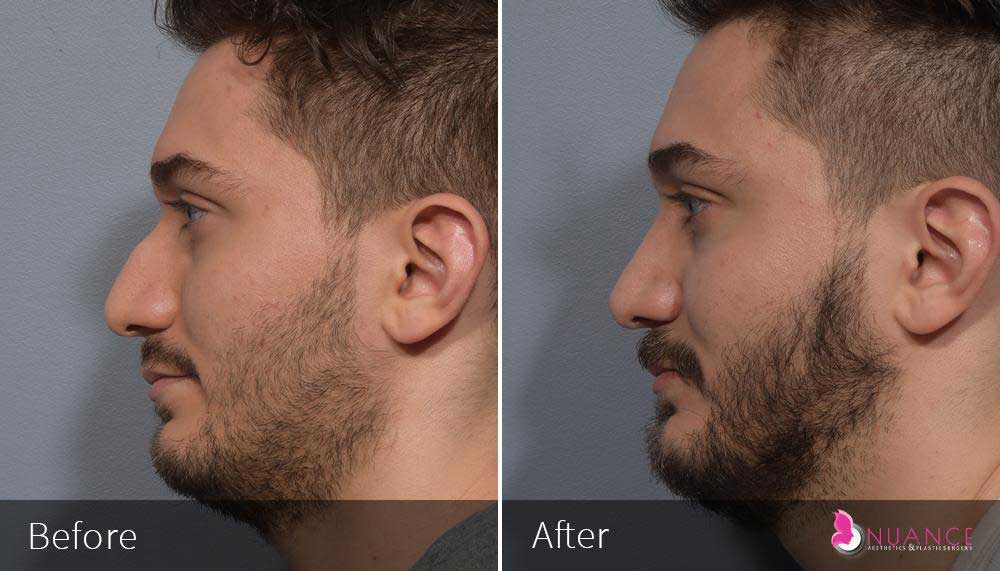
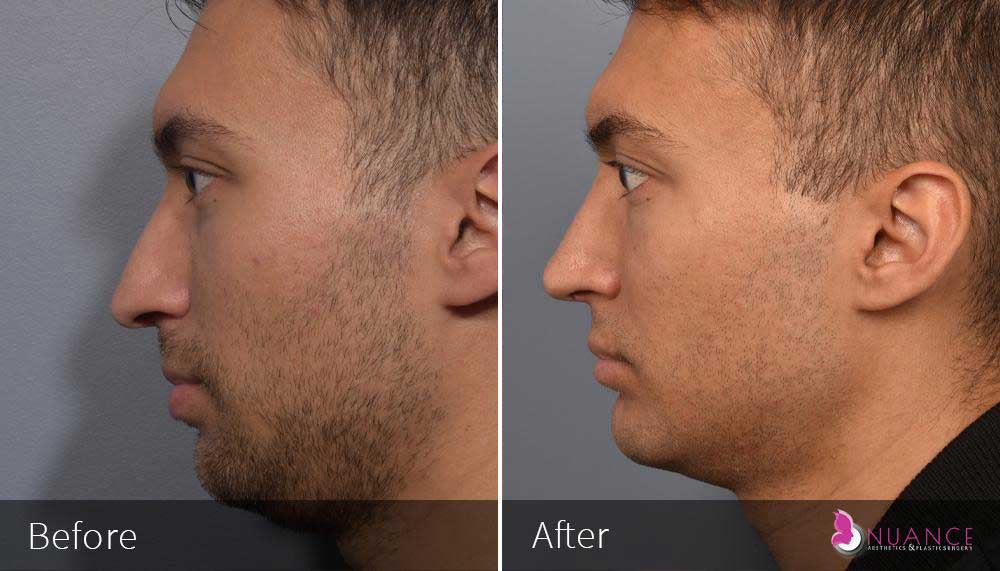
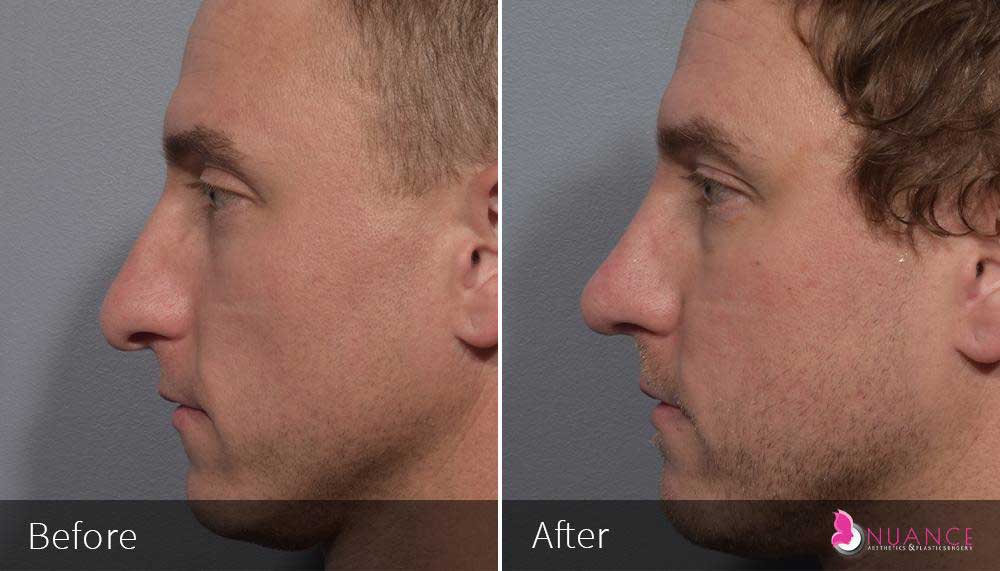
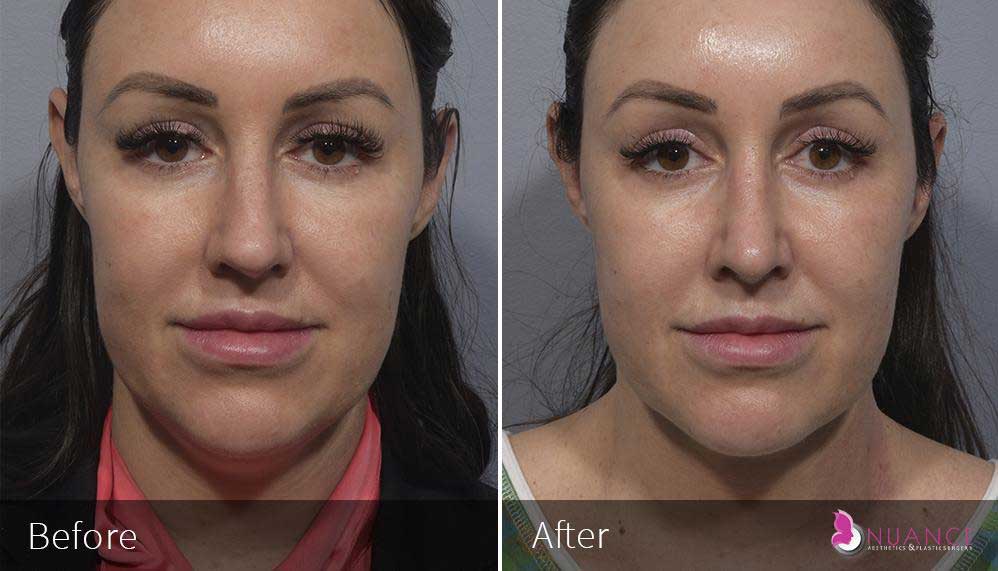
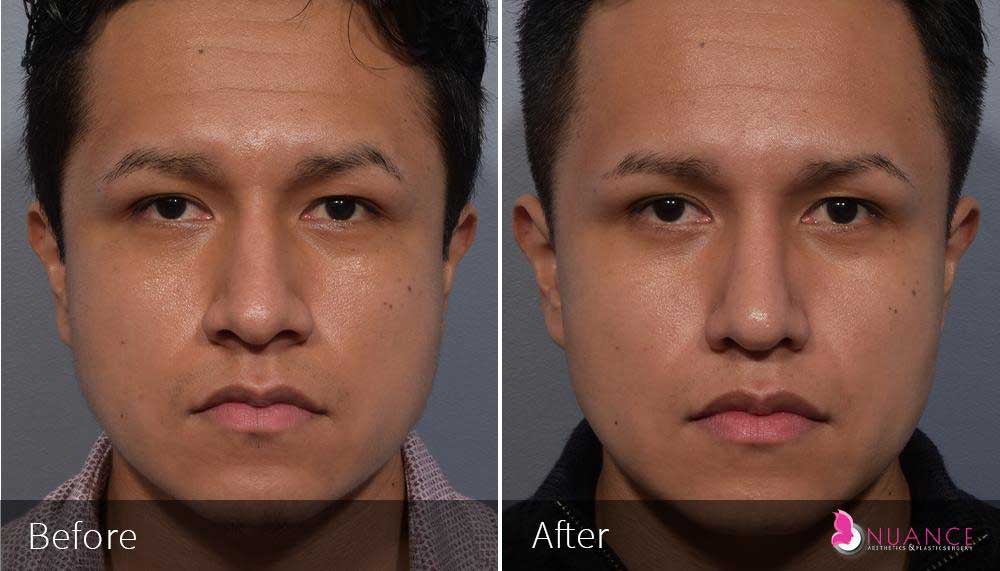
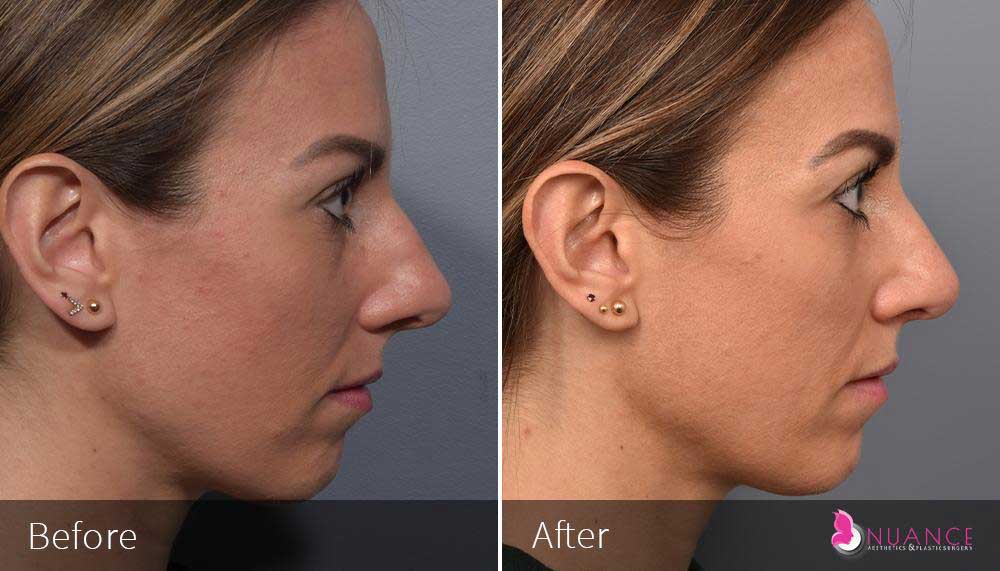
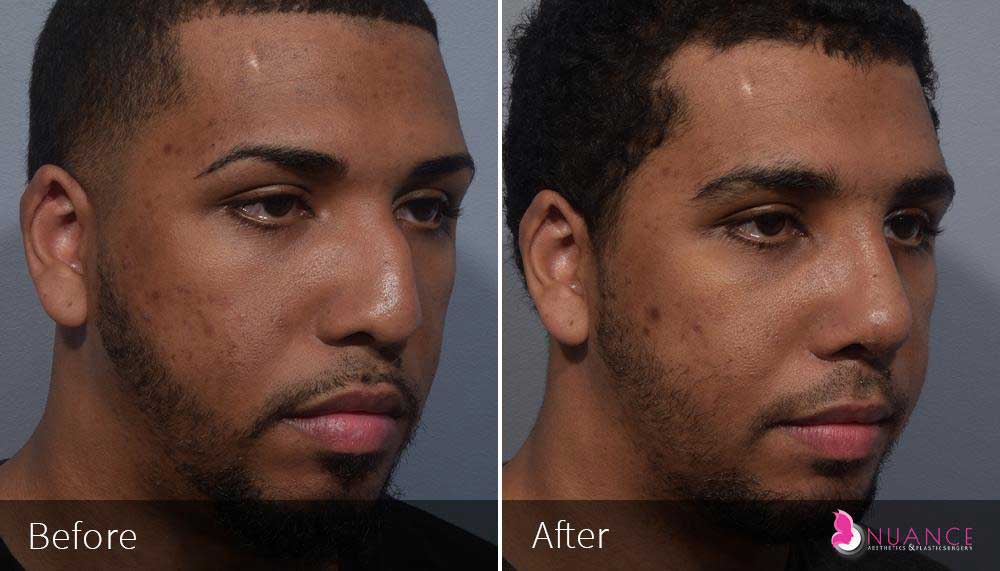
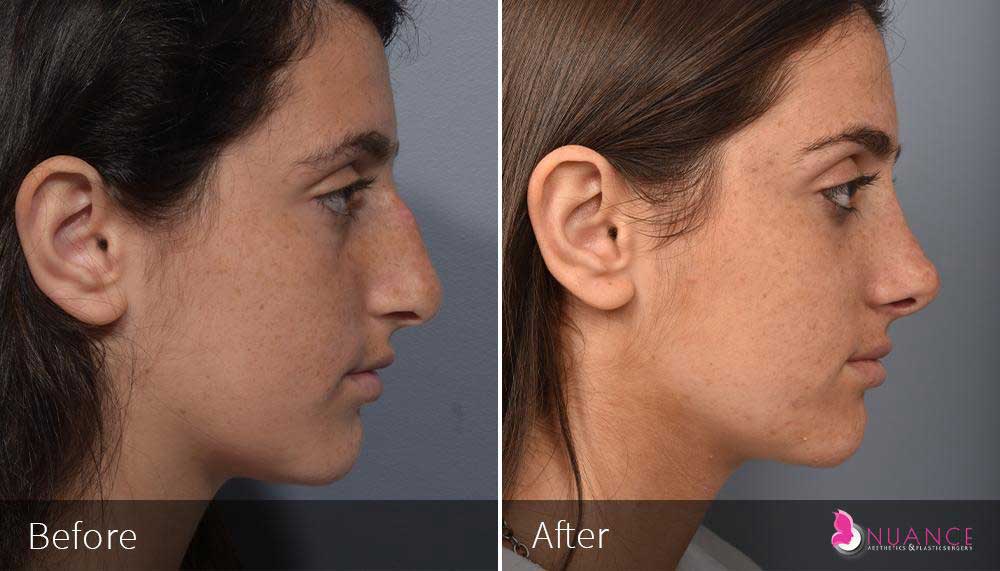
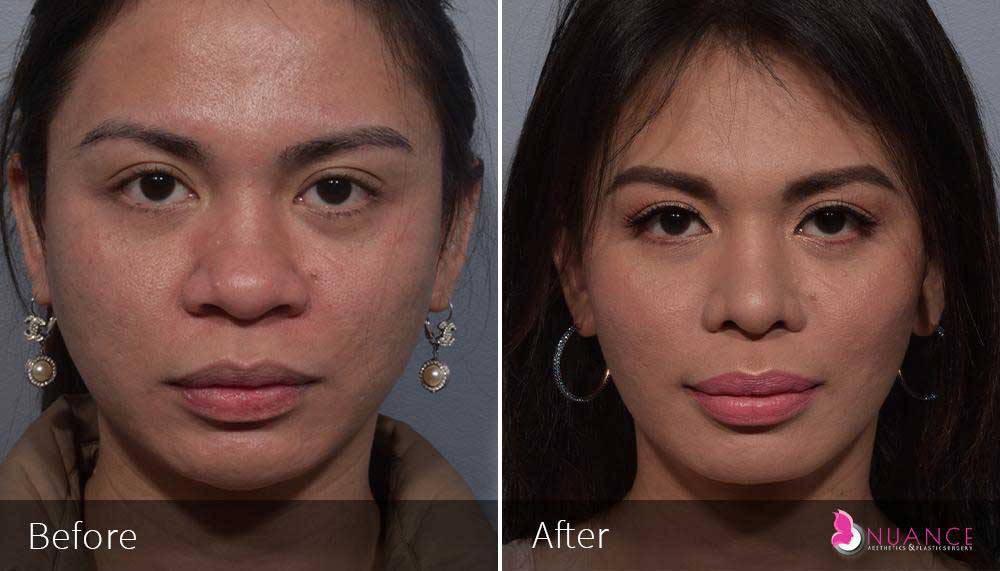
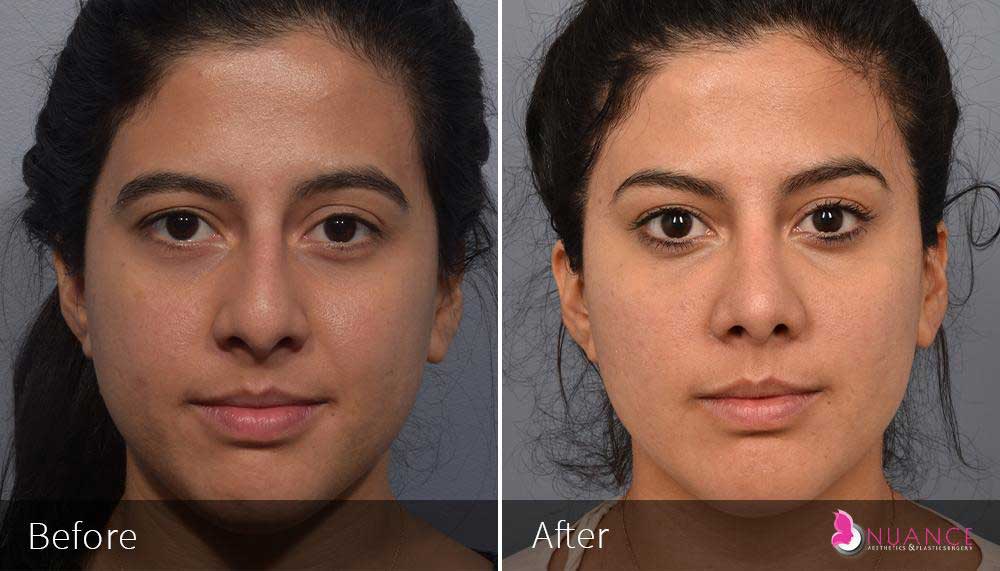
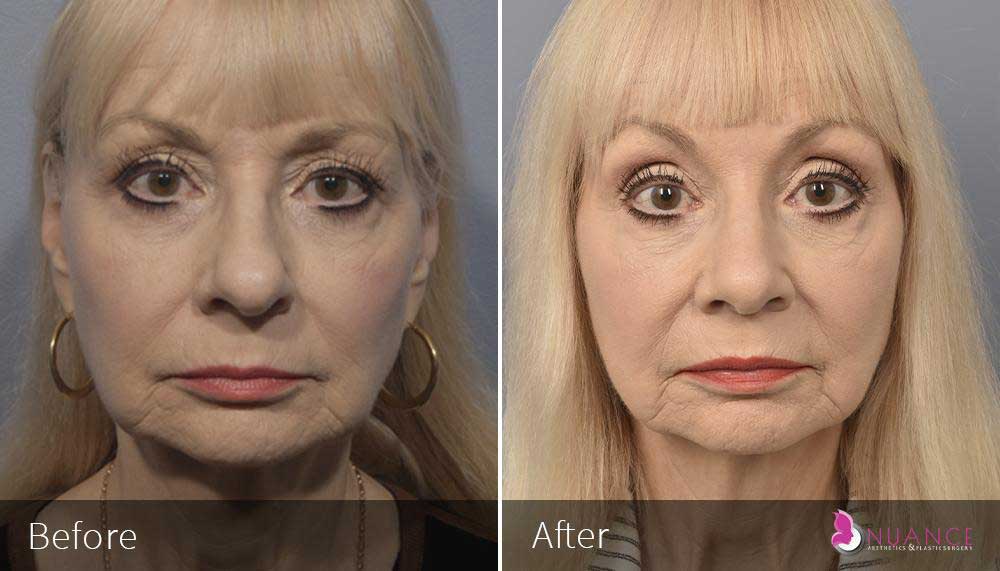
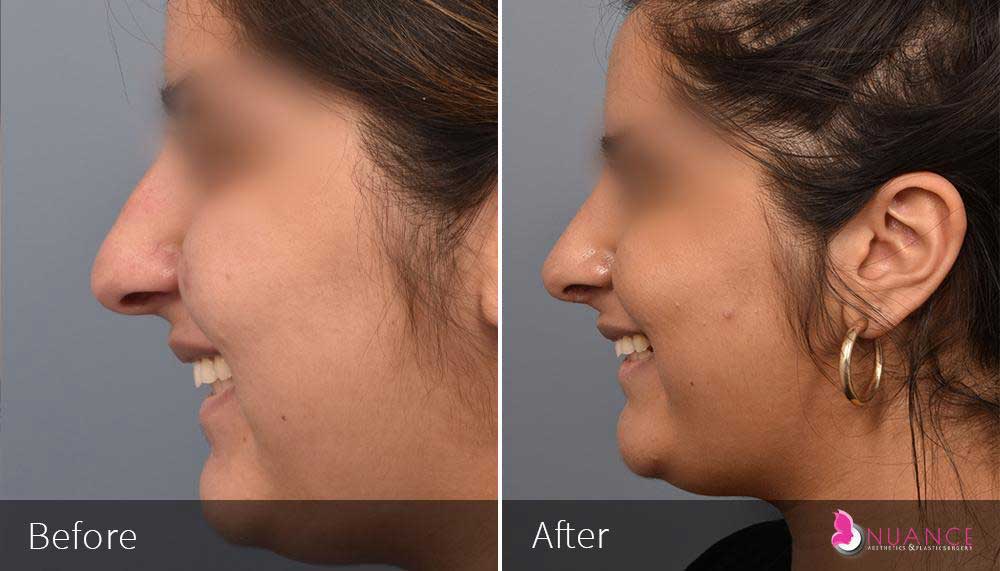
Whether you are a Las Vegas resident or an out-of-town guest, you will find that Nuance Aesthetics & Plastic Surgery stands out among other practices. Dr. Jeannie Khavkin is a fellowship-trained facial plastic surgeon using her mastery of facial aging and aesthetics to determine whether a surgical or a non-invasive approach would be better for you. Dr. Sina relocated his practice from Park Avenue on the Upper East Side of Manhattan to Las Vegas. Dr. Sina’s mission is to provide entirely patient-centered care - where each patient is evaluated with special consideration of their unique facial features and receives a customized treatment plan. In addition, our Aesthetics Concierge is at your service, educating our patients and providing individual attention to help you meet your aesthetic goals.